Phospho-IKK epsilon (Ser172) Antibody - #AF8156
| Product: | Phospho-IKK epsilon (Ser172) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF8156 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-IKK epsilon (Ser172) |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 80kDa; 80kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q14164 |
| RRID: | AB_2840218 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF8156, RRID:AB_2840218.
Fold/Unfold
I kappa B kinase epsilon; I-kappa-B kinase epsilon; IkBKE; IKK related kinase epsilon; IKK-E; IKK-epsilon; IKK-i; IKKE; IKKE_HUMAN; IKKepsilon; IKKI; Inducible I kappa B kinase; Inducible I kappa-B kinase; Inducible IkappaB kinase; Inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells kinase epsilon; Inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells, kinase of, epsilon; Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit epsilon; KIAA0151; MGC125294; MGC125295; MGC125297;
Immunogens
Highly expressed in spleen followed by thymus, peripheral blood leukocytes, pancreas, placenta. Weakly expressed in lung, kidney, prostate, ovary and colon.
- Q14164 IKKE_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MQSTANYLWHTDDLLGQGATASVYKARNKKSGELVAVKVFNTTSYLRPREVQVREFEVLRKLNHQNIVKLFAVEETGGSRQKVLVMEYCSSGSLLSVLESPENAFGLPEDEFLVVLRCVVAGMNHLRENGIVHRDIKPGNIMRLVGEEGQSIYKLTDFGAARELDDDEKFVSVYGTEEYLHPDMYERAVLRKPQQKAFGVTVDLWSIGVTLYHAATGSLPFIPFGGPRRNKEIMYRITTEKPAGAIAGAQRRENGPLEWSYTLPITCQLSLGLQSQLVPILANILEVEQAKCWGFDQFFAETSDILQRVVVHVFSLSQAVLHHIYIHAHNTIAIFQEAVHKQTSVAPRHQEYLFEGHLCVLEPSVSAQHIAHTTASSPLTLFSTAIPKGLAFRDPALDVPKFVPKVDLQADYNTAKGVLGAGYQALRLARALLDGQELMFRGLHWVMEVLQATCRRTLEVARTSLLYLSSSLGTERFSSVAGTPEIQELKAAAELRSRLRTLAEVLSRCSQNITETQESLSSLNRELVKSRDQVHEDRSIQQIQCCLDKMNFIYKQFKKSRMRPGLGYNEEQIHKLDKVNFSHLAKRLLQVFQEECVQKYQASLVTHGKRMRVVHETRNHLRLVGCSVAACNTEAQGVQESLSKLLEELSHQLLQDRAKGAQASPPPIAPYPSPTRKDLLLHMQELCEGMKLLASDLLDNNRIIERLNRVPAPPDV
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - Q14164 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| K25 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K30 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K61 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K137 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y153 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K154 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S172 | Phosphorylation | Q14164 (IKBKE) , O14920 (IKBKB) , O15111 (CHUK) | Uniprot |
| Y179 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K231 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K231 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K241 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K401 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K416 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T463 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S464 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T474 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S479 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K490 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T501 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S519 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S522 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K549 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K578 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K609 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S664 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y671 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S673 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K677 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot |
PTMs - Q14164 As Enzyme
| Substrate | Site | Source |
|---|---|---|
| O00571 (DDX3X) | S102 | Uniprot |
| O14519 (CDK2AP1) | S46 | Uniprot |
| O43524 (FOXO3) | S644 | Uniprot |
| O43734 (TRAF3IP2) | S328 | Uniprot |
| O95786 (DDX58) | S855 | Uniprot |
| P03372 (ESR1) | S167 | Uniprot |
| P10914 (IRF1) | S215 | Uniprot |
| P10914 (IRF1) | S219 | Uniprot |
| P10914 (IRF1) | S221 | Uniprot |
| P25963 (NFKBIA) | S32 | Uniprot |
| P25963 (NFKBIA) | S36 | Uniprot |
| P31749 (AKT1) | T308 | Uniprot |
| P31749 (AKT1) | S473 | Uniprot |
| P42224 (STAT1) | S727 | Uniprot |
| P49840 (GSK3A) | S21 | Uniprot |
| P98170 (XIAP) | S430 | Uniprot |
| Q04206 (RELA) | S468 | Uniprot |
| Q04206 (RELA) | S536 | Uniprot |
| Q12933 (TRAF2) | S11 | Uniprot |
| Q14164 (IKBKE) | S172 | Uniprot |
| Q14653 (IRF3) | S386 | Uniprot |
| Q14653 (IRF3) | S396 | Uniprot |
| Q14653 (IRF3) | S398 | Uniprot |
| Q14653 (IRF3) | S402 | Uniprot |
| Q5S007 (LRRK2) | S910 | Uniprot |
| Q5S007 (LRRK2) | S935 | Uniprot |
| Q92844 (TANK) | S49 | Uniprot |
| Q92844 (TANK) | S100 | Uniprot |
| Q92844 (TANK) | S126 | Uniprot |
| Q92844 (TANK) | S178 | Uniprot |
| Q92844 (TANK) | S208 | Uniprot |
| Q92844 (TANK) | S228 | Uniprot |
| Q92844 (TANK) | S257 | Uniprot |
| Q92844 (TANK) | S406 | Uniprot |
| Q92844 (TANK) | S409 | Uniprot |
| Q92985 (IRF7) | S471 | Uniprot |
| Q92985 (IRF7) | S472 | Uniprot |
| Q92985 (IRF7) | S477 | Uniprot |
| Q92985 (IRF7) | S479 | Uniprot |
| Q96FA3 (PELI1) | S76 | Uniprot |
| Q96FA3 (PELI1) | T80 | Uniprot |
| Q96FA3 (PELI1) | T288 | Uniprot |
| Q96FA3 (PELI1) | S293 | Uniprot |
| Q9NQC7 (CYLD) | S418 | Uniprot |
| Q9Y6K9 (IKBKG) | T50 | Uniprot |
| Q9Y6K9 (IKBKG) | S141 | Uniprot |
| Q9Y6K9 (IKBKG) | S148 | Uniprot |
| Q9Y6K9 (IKBKG) | S196 | Uniprot |
| Q9Y6K9 (IKBKG) | S208 | Uniprot |
| Q9Y6K9 (IKBKG) | S247 | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Serine/threonine kinase that plays an essential role in regulating inflammatory responses to viral infection, through the activation of the type I IFN, NF-kappa-B and STAT signaling. Also involved in TNFA and inflammatory cytokines, like Interleukin-1, signaling. Following activation of viral RNA sensors, such as RIG-I-like receptors, associates with DDX3X and phosphorylates interferon regulatory factors (IRFs), IRF3 and IRF7, as well as DDX3X. This activity allows subsequent homodimerization and nuclear translocation of the IRF3 leading to transcriptional activation of pro-inflammatory and antiviral genes including IFNB. In order to establish such an antiviral state, IKBKE forms several different complexes whose composition depends on the type of cell and cellular stimuli. Thus, several scaffolding molecules including IPS1/MAVS, TANK, AZI2/NAP1 or TBKBP1/SINTBAD can be recruited to the IKBKE-containing-complexes. Activated by polyubiquitination in response to TNFA and interleukin-1, regulates the NF-kappa-B signaling pathway through, at least, the phosphorylation of CYLD. Phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B thus leading to the dissociation of the inhibitor/NF-kappa-B complex and ultimately the degradation of the inhibitor. In addition, is also required for the induction of a subset of ISGs which displays antiviral activity, may be through the phosphorylation of STAT1 at 'Ser-708'. Phosphorylation of STAT1 at 'Ser-708' seems also to promote the assembly and DNA binding of ISGF3 (STAT1:STAT2:IRF9) complexes compared to GAF (STAT1:STAT1) complexes, in this way regulating the balance between type I and type II IFN responses. Protects cells against DNA damage-induced cell death. Also plays an important role in energy balance regulation by sustaining a state of chronic, low-grade inflammation in obesity, wich leads to a negative impact on insulin sensitivity. Phosphorylates AKT1.
Autophosphorylated and phosphorylated by IKBKB/IKKB. Phosphorylation at Ser-172 is enhanced by the interaction with DDX3X. Phosphorylated at Thr-501 upon IFN activation.
Sumoylation by TOPORS upon DNA damage is required for protection of cells against DNA damage-induced cell death. Desumoylated by SENP1.
'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitinated at Lys-30 and Lys-401 by TRAF2:BIRC2 and TRAF2:BIRC3 complexes. Ubiquitination is induced by LPS, TNFA and interleukin-1 and required for full kinase activity and KF-kappa-B pathway activation.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Nucleus>PML body.
Note: Targeting to PML nuclear bodies upon DNA damage is TOPORS-dependent (PubMed:20188669). Located diffusely throughout the cytoplasm but locates to punctate cytoplasmic bodies when coexpressed with TRIM6 (PubMed:24882218).
Highly expressed in spleen followed by thymus, peripheral blood leukocytes, pancreas, placenta. Weakly expressed in lung, kidney, prostate, ovary and colon.
Homodimer. Interacts with MAVS/IPS1. Interacts (via protein kinase domain) with TTLL12 (via N-terminus); the interaction prevents MAVS binding to IKBKE. Interacts with the adapter proteins AZI2/NAP1, TANK and TBKBP1/SINTBAD. Interacts with SIKE1. Interacts with TICAM1/TRIF, IRF3 and DDX58/RIG-I; interactions are disrupted by the interaction between IKBKE and SIKE1. Interacts with TOPORS; induced by DNA damage. Interacts with CYLD. Interacts (when polyubiquitinated) with IKBKB, IKBKG and MYD88. Interacts with IFIH1. Interacts with DDX3X; the interaction is found to be induced upon virus infection. Interacts with TRIM6 (via SPRY box). Interacts with unanchored K48-linked polyubiquitin chains; this leads to IKBKE activation. Interacts with TBK1.
(Microbial infection) Interacts (via Protein kinase domain) with arenavirus protein N; the interaction inhibits IKBKE kinase function.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Ebola virus protein VP35; the interaction leads to inhibition of cellular antiviral response by blocking necessary interactions between the IKBKE and MAVS/IPS as well as its substrates IRF3 and IRF7.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with human T-cell leukemia virus 1/HTLV-1 protein HBZ.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Ser/Thr protein kinase family. I-kappa-B kinase subfamily.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
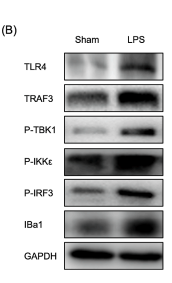
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.