SMURF2 Antibody - #DF7683
| Product: | SMURF2 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7683 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to SMURF2 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 86 kDa; 86kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9HAU4 |
| RRID: | AB_2841154 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7683, RRID:AB_2841154.
Fold/Unfold
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF2; EC 6.3.2.; hSMURF2; MGC138150; Smad specific E3 ubiquitin ligase 2; SMAD specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2; SMAD ubiquitination regulatory factor 2; SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase 2; SMUF2_HUMAN; Smurf2; Ubiquitin protein ligase SMURF2;
Immunogens
- Q9HAU4 SMUF2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSNPGGRRNGPVKLRLTVLCAKNLVKKDFFRLPDPFAKVVVDGSGQCHSTDTVKNTLDPKWNQHYDLYIGKSDSVTISVWNHKKIHKKQGAGFLGCVRLLSNAINRLKDTGYQRLDLCKLGPNDNDTVRGQIVVSLQSRDRIGTGGQVVDCSRLFDNDLPDGWEERRTASGRIQYLNHITRTTQWERPTRPASEYSSPGRPLSCFVDENTPISGTNGATCGQSSDPRLAERRVRSQRHRNYMSRTHLHTPPDLPEGYEQRTTQQGQVYFLHTQTGVSTWHDPRVPRDLSNINCEELGPLPPGWEIRNTATGRVYFVDHNNRTTQFTDPRLSANLHLVLNRQNQLKDQQQQQVVSLCPDDTECLTVPRYKRDLVQKLKILRQELSQQQPQAGHCRIEVSREEIFEESYRQVMKMRPKDLWKRLMIKFRGEEGLDYGGVAREWLYLLSHEMLNPYYGLFQYSRDDIYTLQINPDSAVNPEHLSYFHFVGRIMGMAVFHGHYIDGGFTLPFYKQLLGKSITLDDMELVDPDLHNSLVWILENDITGVLDHTFCVEHNAYGEIIQHELKPNGKSIPVNEENKKEYVRLYVNWRFLRGIEAQFLALQKGFNEVIPQHLLKTFDEKELELIICGLGKIDVNDWKVNTRLKHCTPDSNIVKWFWKAVEFFDEERRARLLQFVTGSSRVPLQGFKALQGAAGPRLFTIHQIDACTNNLPKAHTCFNRIDIPPYESYEKLYEKLLTAIEETCGFAVE
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - Q9HAU4 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| K26 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K38 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S44 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T144 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T168 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S170 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S203 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| R232 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| R234 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| R237 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| R239 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| T249 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K369 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K375 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K377 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S406 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y407 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K412 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y434 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y499 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K578 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K579 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K638 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K730 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K734 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which accepts ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates. Interacts with SMAD1 and SMAD7 in order to trigger their ubiquitination and proteasome-dependent degradation. In addition, interaction with SMAD7 activates autocatalytic degradation, which is prevented by interaction with SCYE1. Forms a stable complex with the TGF-beta receptor-mediated phosphorylated SMAD2 and SMAD3. In this way, SMAD2 may recruit substrates, such as SNON, for ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Enhances the inhibitory activity of SMAD7 and reduces the transcriptional activity of SMAD2. Coexpression of SMURF2 with SMAD1 results in considerable decrease in steady-state level of SMAD1 protein and a smaller decrease of SMAD2 level. Negatively regulates TGFB1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and myofibroblast differentiation.
Auto-ubiquitinated and ubiquitinated in the presence of RNF11 and UBE2D1. Ubiquitinated by the SCF(FBXL15) complex and TTC3, leading to its degradation by the proteasome.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Membrane raft.
Note: Cytoplasmic in the presence of SMAD7. Colocalizes with CAV1, SMAD7 and TGF-beta receptor in membrane rafts.
Widely expressed.
Interacts (via WW domains) with SMAD1. Interacts (via WW domains) with SMAD2 (via PY-motif). Interacts (via WW domains) with SMAD3 (via PY-motif). Interacts with SMAD6. Interacts with SMAD7 (via PY-motif) and TGFBR1; SMAD7 recruits SMURF2 to the TGF-beta receptor and regulates its degradation. Does not interact with SMAD4; SMAD4 lacks a PY-motif. Interacts with AIMP1. Interacts with STAMBP and RNF11. Interacts with NDFIP1 and NDFIP2 (Probable); this interaction activates the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. Interacts with TTC3.
The second and third WW domains are responsible for interaction with the PY-motif of R-SMAD (SMAD1, SMAD2 and SMAD3).
The C2 domain is involved in autoinhibition of the catalytic activity by interacting with the HECT domain.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hedgehog signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TGF-beta signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis. (View pathway)
References
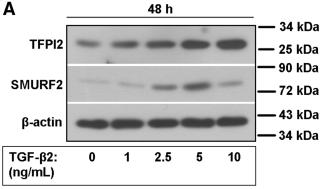
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: pancreatic cancer cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: hRGECs
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.