PDCD6IP Antibody - #DF9027
| Product: | PDCD6IP Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF9027 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to PDCD6IP |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 96 kDa; 96kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q8WUM4 |
| RRID: | AB_2842223 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF9027, RRID:AB_2842223.
Fold/Unfold
AIP1; ALG 2 interacting protein 1; ALG-2-interacting protein 1; ALG2 interacting protein X; Alix; Apoptosis linked gene 2 interacting protein X; Dopamine receptor interacting protein 4; DRIP4; Hp95; KIAA1375; MGC17003; PDC6I_HUMAN; PDCD6 interacting protein; PDCD6-interacting protein; PDCD6IP; Programmed cell death 6 interacting protein; Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein;
Immunogens
- Q8WUM4 PDC6I_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MATFISVQLKKTSEVDLAKPLVKFIQQTYPSGGEEQAQYCRAAEELSKLRRAAVGRPLDKHEGALETLLRYYDQICSIEPKFPFSENQICLTFTWKDAFDKGSLFGGSVKLALASLGYEKSCVLFNCAALASQIAAEQNLDNDEGLKIAAKHYQFASGAFLHIKETVLSALSREPTVDISPDTVGTLSLIMLAQAQEVFFLKATRDKMKDAIIAKLANQAADYFGDAFKQCQYKDTLPKEVFPVLAAKHCIMQANAEYHQSILAKQQKKFGEEIARLQHAAELIKTVASRYDEYVNVKDFSDKINRALAAAKKDNDFIYHDRVPDLKDLDPIGKATLVKSTPVNVPISQKFTDLFEKMVPVSVQQSLAAYNQRKADLVNRSIAQMREATTLANGVLASLNLPAAIEDVSGDTVPQSILTKSRSVIEQGGIQTVDQLIKELPELLQRNREILDESLRLLDEEEATDNDLRAKFKERWQRTPSNELYKPLRAEGTNFRTVLDKAVQADGQVKECYQSHRDTIVLLCKPEPELNAAIPSANPAKTMQGSEVVNVLKSLLSNLDEVKKEREGLENDLKSVNFDMTSKFLTALAQDGVINEEALSVTELDRVYGGLTTKVQESLKKQEGLLKNIQVSHQEFSKMKQSNNEANLREEVLKNLATAYDNFVELVANLKEGTKFYNELTEILVRFQNKCSDIVFARKTERDELLKDLQQSIAREPSAPSIPTPAYQSSPAGGHAPTPPTPAPRTMPPTKPQPPARPPPPVLPANRAPSATAPSPVGAGTAAPAPSQTPGSAPPPQAQGPPYPTYPGYPGYCQMPMPMGYNPYAYGQYNMPYPPVYHQSPGQAPYPGPQQPSYPFPQPPQQSYYPQQ
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - Q8WUM4 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K10 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| S13 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K19 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K23 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K23 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y39 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| C40 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| K48 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K48 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K60 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K60 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K101 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S103 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S108 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T166 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S169 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T186 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K209 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K215 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K215 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y223 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K229 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K234 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K239 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| C250 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| Y258 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K269 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K285 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y294 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K298 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K303 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K313 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y319 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| R322 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| K327 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K334 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K339 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K350 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K350 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K357 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S366 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y370 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K438 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| R456 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| T464 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K471 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T479 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S481 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y485 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K486 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K486 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K501 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K510 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K541 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K563 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S575 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| R606 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| Y608 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T612 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T613 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K614 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K627 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K638 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K640 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S692 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K707 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S712 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S718 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S721 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T724 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y727 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S729 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S730 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T738 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T741 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| R745 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| K751 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K751 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| K751 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| R757 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| R767 | Methylation | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Multifunctional protein involved in endocytosis, multivesicular body biogenesis, membrane repair, cytokinesis, apoptosis and maintenance of tight junction integrity. Class E VPS protein involved in concentration and sorting of cargo proteins of the multivesicular body (MVB) for incorporation into intralumenal vesicles (ILVs) that are generated by invagination and scission from the limiting membrane of the endosome. Binds to the phospholipid lysobisphosphatidic acid (LBPA) which is abundant in MVBs internal membranes. The MVB pathway requires the sequential function of ESCRT-O, -I,-II and -III complexes. The ESCRT machinery also functions in topologically equivalent membrane fission events, such as the terminal stages of cytokinesis. Adapter for a subset of ESCRT-III proteins, such as CHMP4, to function at distinct membranes. Required for completion of cytokinesis. May play a role in the regulation of both apoptosis and cell proliferation. Regulates exosome biogenesis in concert with SDC1/4 and SDCBP. By interacting with F-actin, PARD3 and TJP1 secures the proper assembly and positioning of actomyosin-tight junction complex at the apical sides of adjacent epithelial cells that defines a spatial membrane domain essential for the maintenance of epithelial cell polarity and barrier (By similarity).
(Microbial infection) Involved in HIV-1 virus budding. Can replace TSG101 it its role of supporting HIV-1 release; this function requires the interaction with CHMP4B. The ESCRT machinery also functions in topologically equivalent membrane fission events, such as enveloped virus budding (HIV-1 and other lentiviruses).
May be phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by activated PDGFRB.
Cytoplasm>Cytosol. Melanosome. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome. Secreted>Extracellular exosome. Cell junction>Tight junction. Midbody>Midbody ring.
Note: Identified by mass spectrometry in melanosome fractions from stage I to stage IV. Colocalized with CEP55 at centrosomes of non-dividing cells. Component of the actomyosin-tight junction complex (By similarity). PDCD6IP targeting to the midbody requires the interaction with CEP55 (PubMed:18641129).
Self-associates. Interacts with SH3KBP1/CIN85 (By similarity). Interacts with PDCD6 in a calcium -dependent manner. Interacts with TSG101 in a calcium-dependent manner; PDCD6IP homooligomerization may be required for TSG101-binding. Interacts with SGSM3. Directly interacts with CHMP4A, CHMP4B and CHMP4C. Directly interacts with CEP55 in a 1:2 stoechiometry. The interaction with CEP55 is required for PDCD6IP targeting to the midbody. May interact with PDGFRB. Interacts with SH3GL1 and SH3GL2/endophilin-1. Forms a complex with SDCBP and SDC2. Found in a complex with F-actin, TJP1/ZO-1 and PARD3 (By similarity). Interacts with CD2AP. Interacts with ARRDC1.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with HIV-1 p6. Interacts with HIV-1 p9.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with EIAV p9.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Murine leukemia virus Gag polyprotein (via LYPX(n)L motif).
(Microbial infection) Interacts with ebola virus protein VP40 (via YPx(n)L/I motif).
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
References
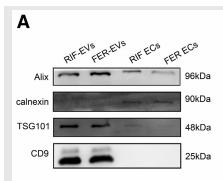
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: RIF-EVs and FER-EVs.
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: lung tissues
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: granulosa cells
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.