PRDM16 Antibody - #DF13303
| Product: | PRDM16 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF13303 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to PRDM16 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 70~140kDa; 140kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9HAZ2 |
| RRID: | AB_2846322 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF13303, RRID:AB_2846322.
Fold/Unfold
CMD1LL; KIAA1675; LVNC8; MDS1/EVI1 like gene 1; MDS1/EVI1-like gene 1; MEL1; PFM 13; PFM13; PR domain containing 16; PR domain containing protein 16; PR domain zinc finger protein 16; PR domain-containing protein 16; PRD16_HUMAN; Prdm16; Transcription factor MEL 1; Transcription factor MEL1;
Immunogens
Expressed in uterus and kidney. Expressed in both cardiomyocytes and interstitial cells.
- Q9HAZ2 PRD16_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MRSKARARKLAKSDGDVVNNMYEPNRDLLASHSAEDEAEDSAMSPIPVGPPSPFPTSEDFTPKEGSPYEAPVYIPEDIPIPADFELRESSIPGAGLGVWAKRKMEAGERLGPCVVVPRAAAKETDFGWEQILTDVEVSPQEGCITKISEDLGSEKFCVDANQAGAGSWLKYIRVACSCDDQNLTMCQISEQIYYKVIKDIEPGEELLVHVKEGVYPLGTVPPGLDEEPTFRCDECDELFQSKLDLRRHKKYTCGSVGAALYEGLAEELKPEGLGGGSGQAHECKDCERMFPNKYSLEQHMVIHTEEREYKCDQCPKAFNWKSNLIRHQMSHDSGKRFECENCVKVFTDPSNLQRHIRSQHVGARAHACPDCGKTFATSSGLKQHKHIHSTVKPFICEVCHKSYTQFSNLCRHKRMHADCRTQIKCKDCGQMFSTTSSLNKHRRFCEGKNHYTPGGIFAPGLPLTPSPMMDKAKPSPSLNHASLGFNEYFPSRPHPGSLPFSTAPPTFPALTPGFPGIFPPSLYPRPPLLPPTSLLKSPLNHTQDAKLPSPLGNPALPLVSAVSNSSQGTTAAAGPEEKFESRLEDSCVEKLKTRSSDMSDGSDFEDVNTTTGTDLDTTTGTGSDLDSDVDSDPDKDKGKGKSAEGQPKFGGGLAPPGAPNSVAEVPVFYSQHSFFPPPDEQLLTATGAAGDSIKAIASIAEKYFGPGFMGMQEKKLGSLPYHSAFPFQFLPNFPHSLYPFTDRALAHNLLVKAEPKSPRDALKVGGPSAECPFDLTTKPKDVKPILPMPKGPSAPASGEEQPLDLSIGSRARASQNGGGREPRKNHVYGERKLGAGEGLPQVCPARMPQQPPLHYAKPSPFFMDPIYSRVEKRKVTDPVGALKEKYLRPSPLLFHPQMSAIETMTEKLESFAAMKADSGSSLQPLPHHPFNFRSPPPTLSDPILRKGKERYTCRYCGKIFPRSANLTRHLRTHTGEQPYRCKYCDRSFSISSNLQRHVRNIHNKEKPFKCHLCNRCFGQQTNLDRHLKKHEHENAPVSQHPGVLTNHLGTSASSPTSESDNHALLDEKEDSYFSEIRNFIANSEMNQASTRTEKRADMQIVDGSAQCPGLASEKQEDVEEEDDDDLEEDDEDSLAGKSQDDTVSPAPEPQAAYEDEEDEEPAASLAVGFDHTRRCAEDHEGGLLALEPMPTFGKGLDLRRAAEEAFEVKDVLNSTLDSEALKHTLCRQAKNQAYAMMLSLSEDTPLHTPSQGSLDAWLKVTGATSESGAFHPINHL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - Q9HAZ2 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| S44 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S52 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S66 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y193 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y194 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K321 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| S379 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K382 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| T421 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S433 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T434 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T435 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T464 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S537 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S581 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S586 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T611 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K778 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T876 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K915 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| T974 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S989 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1089 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T1090 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K1194 | Acetylation | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Binds DNA and functions as a transcriptional regulator. Displays histone methyltransferase activity and monomethylates 'Lys-9' of histone H3 (H3K9me1) in vitro (By similarity). Probably catalyzes the monomethylation of free histone H3 in the cytoplasm which is then transported to the nucleus and incorporated into nucleosomes where SUV39H methyltransferases use it as a substrate to catalyze histone H3 'Lys-9' trimethylation (By similarity). Likely to be one of the primary histone methyltransferases along with MECOM/PRDM3 that direct cytoplasmic H3K9me1 methylation (By similarity). Functions in the differentiation of brown adipose tissue (BAT) which is specialized in dissipating chemical energy in the form of heat in response to cold or excess feeding while white adipose tissue (WAT) is specialized in the storage of excess energy and the control of systemic metabolism (By similarity). Together with CEBPB, regulates the differentiation of myoblastic precursors into brown adipose cells (By similarity). Functions as a repressor of TGF-beta signaling.
Binds DNA and functions as a transcriptional regulator. Functions as a repressor of TGF-beta signaling. May regulate granulocyte differentiation.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
Expressed in uterus and kidney. Expressed in both cardiomyocytes and interstitial cells.
Interacts with CEBPA, CEBPB and CEBPD; the interaction is direct. Interacts with PPARG and PPARA; controls brown adipocytes differentiation. Interacts with CTBP1 and CTBP2; represses the expression of WAT-specific genes. Interacts with PPARGC1A and PPARGC1B; interaction with PPARGC1A or PPARGC1B activates the transcription of BAT-specific gene (By similarity). Interacts with HDAC1, SKI, SMAD2 and SMAD3; the interaction with SKI promotes the recruitment of SMAD3-HDAC1 complex on the promoter of TGF-beta target genes. Interacts with ZNF516; the interaction is direct and may play a role in the transcription of brown adipose tissue-specific gene.
Belongs to the PRDM16 family.
References
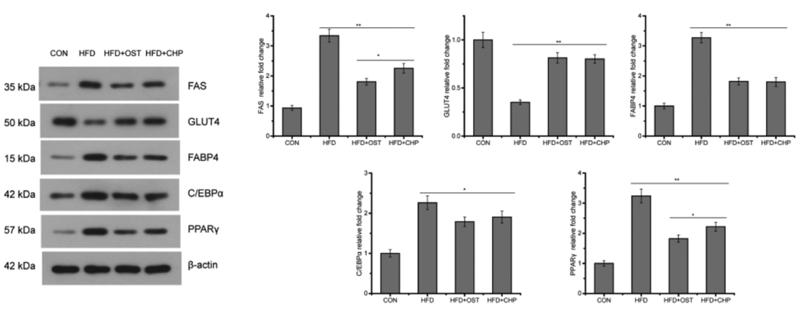
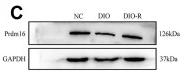
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: white adipose
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: white adipose
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: adipose tissue
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.