GABA A Receptor beta 1 Antibody - #AF6207
| Product: | GABA A Receptor beta 1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6207 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to GABA A Receptor beta 1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 54kDa; 54kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P18505 |
| RRID: | AB_2835088 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6207, RRID:AB_2835088.
Fold/Unfold
AW061132; B230208N19Rik; GABA(A) receptor beta 1; GABA(A) receptor subunit beta-1; GABA-A receptor, beta-1 polypeptide; Gabrb-1; GABRB1; Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor beta 1; Gamma Aminobutyric Acid A Receptor Beta 1; Gamma Aminobutyric Acid Receptor , beta-1; Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, subunit beta 1; Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit beta-1; GARB1; GBRB1_HUMAN;
Immunogens
- P18505 GBRB1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MWTVQNRESLGLLSFPVMITMVCCAHSTNEPSNMSYVKETVDRLLKGYDIRLRPDFGGPPVDVGMRIDVASIDMVSEVNMDYTLTMYFQQSWKDKRLSYSGIPLNLTLDNRVADQLWVPDTYFLNDKKSFVHGVTVKNRMIRLHPDGTVLYGLRITTTAACMMDLRRYPLDEQNCTLEIESYGYTTDDIEFYWNGGEGAVTGVNKIELPQFSIVDYKMVSKKVEFTTGAYPRLSLSFRLKRNIGYFILQTYMPSTLITILSWVSFWINYDASAARVALGITTVLTMTTISTHLRETLPKIPYVKAIDIYLMGCFVFVFLALLEYAFVNYIFFGKGPQKKGASKQDQSANEKNKLEMNKVQVDAHGNILLSTLEIRNETSGSEVLTSVSDPKATMYSYDSASIQYRKPLSSREAYGRALDRHGVPSKGRIRRRASQLKVKIPDLTDVNSIDKWSRMFFPITFSLFNVVYWLYYVH
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - P18505 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| K46 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T85 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K127 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K128 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K137 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y309 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y324 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S409 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S434 | Phosphorylation | P17612 (PRKACA) | Uniprot |
| S448 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Component of the heteropentameric receptor for GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain. Functions also as histamine receptor and mediates cellular responses to histamine. Functions as receptor for diazepines and various anesthetics, such as pentobarbital; these are bound at a separate allosteric effector binding site. Functions as ligand-gated chloride channel.
Cell junction>Synapse>Postsynaptic cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein.
Binds UBQLN1 (By similarity). Heteropentamer, formed by a combination of alpha, beta, gamma, delta and rho chains. Interacts with KCTD8, KCTD12 and KCTD16; this interaction determines the pharmacology and kinetics of the receptor response, the KCTD proteins markedly accelerating the GABA-B response, although to different extents (By similarity).
Belongs to the ligand-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.9) family. Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor (TC 1.A.9.5) subfamily. GABRB1 sub-subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Morphine addiction.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Serotonergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > GABAergic synapse.
References
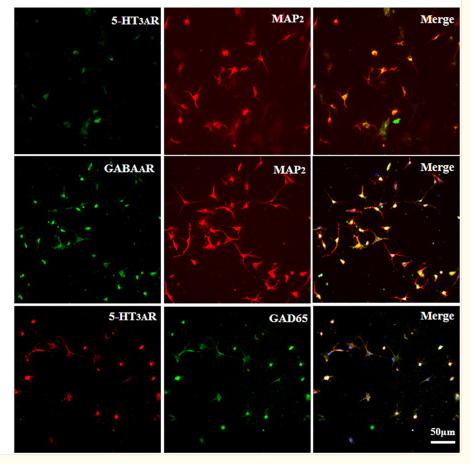
Application: IF/ICC Species: Rat Sample: cholestasis rats
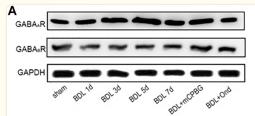
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: spinal cords
Application: IHC Species: Human Sample: ovarian granulosa cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: hippocampus tissue
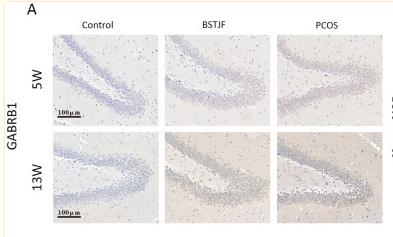
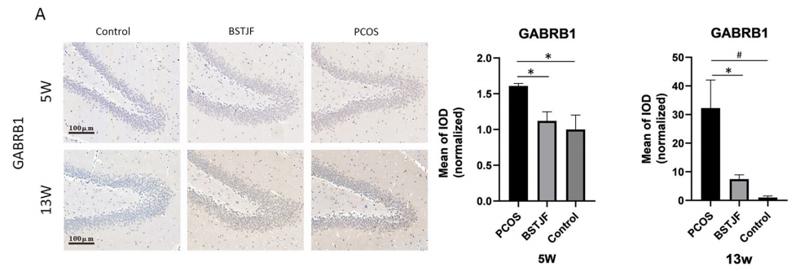
Application: IHC Species: rat Sample: dentate gyrus
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: hippocampus
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: brain tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.