JAM1 Antibody - #DF6373
| Product: | JAM1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6373 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to JAM1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 33kDa; 33kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9Y624 |
| RRID: | AB_2838337 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6373, RRID:AB_2838337.
Fold/Unfold
CD 321; CD321; CD321 antigen; ESTM33; F11 receptor; F11R; JAM 1; JAM A; JAM; JAM-1; JAM-A; JAM1; JAM1_HUMAN; JAMA; JCAM; Jcam1; Junction adhesion molecule 1; Junction adhesion molecule, mouse, homolog of; Junctional adhesion molecule 1; Junctional adhesion molecule A; KAT; Ly106; PAM 1; PAM-1; PAM1; Platelet adhesion molecule 1; Platelet adhesion molecule; Platelet F11 receptor; PRO301; UNQ264;
Immunogens
- Q9Y624 JAM1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MGTKAQVERKLLCLFILAILLCSLALGSVTVHSSEPEVRIPENNPVKLSCAYSGFSSPRVEWKFDQGDTTRLVCYNNKITASYEDRVTFLPTGITFKSVTREDTGTYTCMVSEEGGNSYGEVKVKLIVLVPPSKPTVNIPSSATIGNRAVLTCSEQDGSPPSEYTWFKDGIVMPTNPKSTRAFSNSSYVLNPTTGELVFDPLSASDTGEYSCEARNGYGTPMTSNAVRMEAVERNVGVIVAAVLVTLILLGILVFGIWFAYSRGHFDRTKKGTSSKKVIYSQPSARSEGEFKQTSSFLV
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - Q9Y624 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| R86 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| K97 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S98 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T100 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S133 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T175 | O-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| K178 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| N185 | N-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| S262 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T273 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S275 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K277 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y280 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S281 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S284 | Phosphorylation | P17252 (PRKCA) | Uniprot |
| S287 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K292 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S295 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S296 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Seems to play a role in epithelial tight junction formation. Appears early in primordial forms of cell junctions and recruits PARD3. The association of the PARD6-PARD3 complex may prevent the interaction of PARD3 with JAM1, thereby preventing tight junction assembly (By similarity). Plays a role in regulating monocyte transmigration involved in integrity of epithelial barrier (By similarity). Ligand for integrin alpha-L/beta-2 involved in memory T-cell and neutrophil transmigration. Involved in platelet activation.
(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Mammalian reovirus sigma-1.
(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Human Rotavirus strain Wa.
N-glycosylated.
Cell junction>Tight junction. Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein.
Note: Localized at tight junctions of both epithelial and endothelial cells.
Expressed in endothelium, epithelium and leukocytes (at protein level).
Interacts with the ninth PDZ domain of MPDZ. Interacts with the first PDZ domain of PARD3. The association between PARD3 and PARD6B probably disrupts this interaction (By similarity). Interacts with ITGAL (via I-domain).
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Mammalian reovirus sigma-1 capsid protein.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Human Rotavirus strain Wa vp4 capsid protein.
The Ig-like V-type 2 domain is necessary and sufficient for interaction with integrin alpha-L/beta-2.
Belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs). (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Leukocyte transendothelial migration. (View pathway)
References
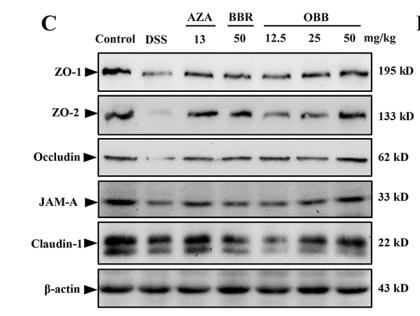
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: colonic tissues
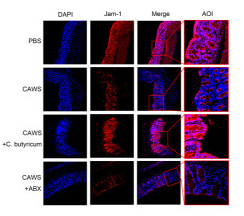
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample:
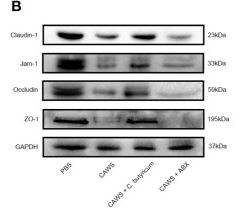
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.