NOS3 Antibody - #DF6450
| Product: | NOS3 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF6450 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to NOS3 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 133kDa; 133kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P29474 |
| RRID: | AB_2838413 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF6450, RRID:AB_2838413.
Fold/Unfold
cNOS; Constitutive NOS; EC NOS; EC-NOS; ecNOS; Endothelial nitric oxidase synthase; Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; Endothelial nitric oxide synthase 3; Endothelial NOS; eNOS; Nitric oxide synthase 3 (endothelial cell); Nitric oxide synthase 3; Nitric oxide synthase 3 endothelial cell; Nitric oxide synthase endothelial; Nitric oxide synthase, endothelial; NOS 3; NOS III; NOS type III; NOS3; NOS3_HUMAN; NOSIII;
Immunogens
- P29474 NOS3_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MGNLKSVAQEPGPPCGLGLGLGLGLCGKQGPATPAPEPSRAPASLLPPAPEHSPPSSPLTQPPEGPKFPRVKNWEVGSITYDTLSAQAQQDGPCTPRRCLGSLVFPRKLQGRPSPGPPAPEQLLSQARDFINQYYSSIKRSGSQAHEQRLQEVEAEVAATGTYQLRESELVFGAKQAWRNAPRCVGRIQWGKLQVFDARDCRSAQEMFTYICNHIKYATNRGNLRSAITVFPQRCPGRGDFRIWNSQLVRYAGYRQQDGSVRGDPANVEITELCIQHGWTPGNGRFDVLPLLLQAPDDPPELFLLPPELVLEVPLEHPTLEWFAALGLRWYALPAVSNMLLEIGGLEFPAAPFSGWYMSTEIGTRNLCDPHRYNILEDVAVCMDLDTRTTSSLWKDKAAVEINVAVLHSYQLAKVTIVDHHAATASFMKHLENEQKARGGCPADWAWIVPPISGSLTPVFHQEMVNYFLSPAFRYQPDPWKGSAAKGTGITRKKTFKEVANAVKISASLMGTVMAKRVKATILYGSETGRAQSYAQQLGRLFRKAFDPRVLCMDEYDVVSLEHETLVLVVTSTFGNGDPPENGESFAAALMEMSGPYNSSPRPEQHKSYKIRFNSISCSDPLVSSWRRKRKESSNTDSAGALGTLRFCVFGLGSRAYPHFCAFARAVDTRLEELGGERLLQLGQGDELCGQEEAFRGWAQAAFQAACETFCVGEDAKAAARDIFSPKRSWKRQRYRLSAQAEGLQLLPGLIHVHRRKMFQATIRSVENLQSSKSTRATILVRLDTGGQEGLQYQPGDHIGVCPPNRPGLVEALLSRVEDPPAPTEPVAVEQLEKGSPGGPPPGWVRDPRLPPCTLRQALTFFLDITSPPSPQLLRLLSTLAEEPREQQELEALSQDPRRYEEWKWFRCPTLLEVLEQFPSVALPAPLLLTQLPLLQPRYYSVSSAPSTHPGEIHLTVAVLAYRTQDGLGPLHYGVCSTWLSQLKPGDPVPCFIRGAPSFRLPPDPSLPCILVGPGTGIAPFRGFWQERLHDIESKGLQPTPMTLVFGCRCSQLDHLYRDEVQNAQQRGVFGRVLTAFSREPDNPKTYVQDILRTELAAEVHRVLCLERGHMFVCGDVTMATNVLQTVQRILATEGDMELDEAGDVIGVLRDQQRYHEDIFGLTLRTQEVTSRIRTQSFSLQERQLRGAVPWAFDPPGSDTNSP
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
PTMs - P29474 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| K5 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| T33 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S53 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y81 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| C94 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| C99 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| S102 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S114 | Phosphorylation | Q00535 (CDK5) | Uniprot |
| C184 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| C201 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| Y210 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| C212 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| S260 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T495 | Phosphorylation | Q04759 (PRKCQ) , Q13237 (PRKG2) , P05771 (PRKCB) , P17612 (PRKACA) , Q02156 (PRKCE) , O75116 (ROCK2) , P17252 (PRKCA) , P05129 (PRKCG) , P24723 (PRKCH) , Q05655 (PRKCD) , Q13131 (PRKAA1) , P41743 (PRKCI) , Q05513 (PRKCZ) | Uniprot |
| S508 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T512 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S615 | Phosphorylation | P17612 (PRKACA) , Q9Y243 (AKT3) , P31751 (AKT2) , P31749 (AKT1) | Uniprot |
| S633 | Phosphorylation | Q13237 (PRKG2) , P54646 (PRKAA2) , Q13131 (PRKAA1) , P17612 (PRKACA) | Uniprot |
| S634 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T636 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S638 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y657 | Phosphorylation | Q14289 (PTK2B) | Uniprot |
| C661 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| S738 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K773 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| C802 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| K834 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S836 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| C853 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| T854 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S870 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K904 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| C976 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| C991 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| K1035 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| C1048 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| C1050 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| K1085 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T1094 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| C1114 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| T1175 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S1177 | O-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| S1177 | Phosphorylation | P22612 (PRKACG) , Q9Y478 (PRKAB1) , P31749 (AKT1) , Q13131 (PRKAA1) , P54646 (PRKAA2) , Q13237 (PRKG2) , P17612 (PRKACA) | Uniprot |
| S1179 | Phosphorylation | P31749 (AKT1) | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is implicated in vascular smooth muscle relaxation through a cGMP-mediated signal transduction pathway. NO mediates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced angiogenesis in coronary vessels and promotes blood clotting through the activation of platelets.
Lacks eNOS activity, dominant-negative form that may down-regulate eNOS activity by forming heterodimers with isoform 1.
Phosphorylation by AMPK at Ser-1177 in the presence of Ca(2+)-calmodulin (CaM) activates activity. In absence of Ca(2+)-calmodulin, AMPK also phosphorylates Thr-495, resulting in inhibition of activity (By similarity). Phosphorylation of Ser-114 by CDK5 reduces activity.
Cell membrane. Membrane>Caveola. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton. Golgi apparatus.
Note: Specifically associates with actin cytoskeleton in the G2 phase of the cell cycle; which is favored by interaction with NOSIP and results in a reduced enzymatic activity.
Platelets, placenta, liver and kidney.
Homodimer. Interacts with NOSIP and NOSTRIN. Interacts with HSP90AB1.
Belongs to the NOS family.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Calcium signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Sphingolipid signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Insulin resistance.
· Metabolism > Amino acid metabolism > Arginine biosynthesis.
· Metabolism > Amino acid metabolism > Arginine and proline metabolism.
· Metabolism > Global and overview maps > Metabolic pathways.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Platelet activation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
References
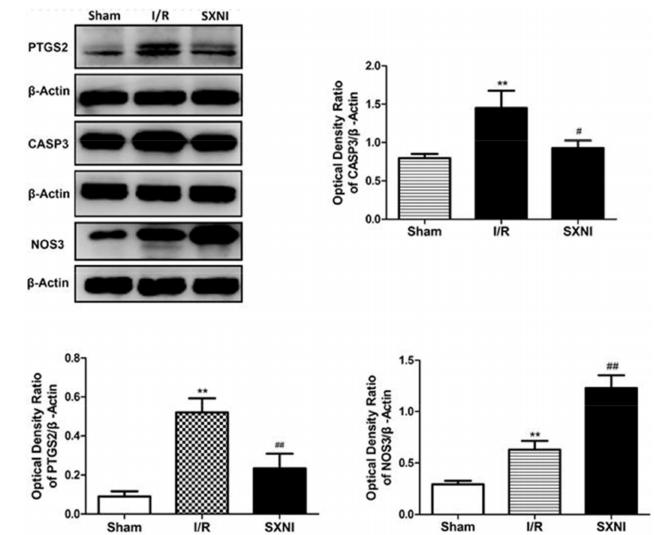
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: hippocampal
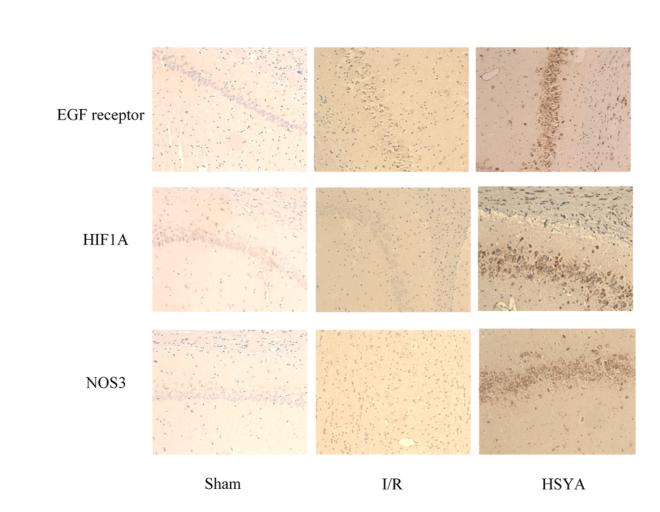
Application: IHC Species: Rat Sample: brain tissue
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.