GAPDH Antibody - #T0004
| Product: | GAPDH Antibody |
| Catalog: | T0004 |
| Description: | Mouse monoclonal antibody to GAPDH |
| Application: | WB ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Pig, Bovine, Sheep, Rabbit, Goat, Guinea pig, Dog, Monkey, Hamster, Chicken, Plants, Rice, Fish |
| Mol.Wt.: | 34KD; 36kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P04406 |
| RRID: | AB_2833041 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# T0004, RRID:AB_2833041.
Fold/Unfold
GAPDH; A1 40 kd subunit; Activator 1 40 kd subunit; G3PD; GAPD; G3pdh; Rfc40; Rf-c 40 kd subunit;
Immunogens
Full-length GAPDH protein of human.
- P04406 G3P_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MGKVKVGVNGFGRIGRLVTRAAFNSGKVDIVAINDPFIDLNYMVYMFQYDSTHGKFHGTVKAENGKLVINGNPITIFQERDPSKIKWGDAGAEYVVESTGVFTTMEKAGAHLQGGAKRVIISAPSADAPMFVMGVNHEKYDNSLKIISNASCTTNCLAPLAKVIHDNFGIVEGLMTTVHAITATQKTVDGPSGKLWRDGRGALQNIIPASTGAAKAVGKVIPELNGKLTGMAFRVPTANVSVVDLTCRLEKPAKYDDIKKVVKQASEGPLKGILGYTEHQVVSSDFNSDTHSSTFDAGAGIALNDHFVKLISWYDNEFGYSNRVVDLMAHMASKE
Research Backgrounds
Has both glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and nitrosylase activities, thereby playing a role in glycolysis and nuclear functions, respectively. Participates in nuclear events including transcription, RNA transport, DNA replication and apoptosis. Nuclear functions are probably due to the nitrosylase activity that mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of nuclear target proteins such as SIRT1, HDAC2 and PRKDC. Modulates the organization and assembly of the cytoskeleton. Facilitates the CHP1-dependent microtubule and membrane associations through its ability to stimulate the binding of CHP1 to microtubules (By similarity). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a key enzyme in glycolysis that catalyzes the first step of the pathway by converting D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) into 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate. Component of the GAIT (gamma interferon-activated inhibitor of translation) complex which mediates interferon-gamma-induced transcript-selective translation inhibition in inflammation processes. Upon interferon-gamma treatment assembles into the GAIT complex which binds to stem loop-containing GAIT elements in the 3'-UTR of diverse inflammatory mRNAs (such as ceruplasmin) and suppresses their translation.
S-nitrosylation of Cys-152 leads to interaction with SIAH1, followed by translocation to the nucleus (By similarity). S-nitrosylation of Cys-247 is induced by interferon-gamma and LDL(ox) implicating the iNOS-S100A8/9 transnitrosylase complex and seems to prevent interaction with phosphorylated RPL13A and to interfere with GAIT complex activity.
ISGylated.
Sulfhydration at Cys-152 increases catalytic activity.
Oxidative stress can promote the formation of high molecular weight disulfide-linked GAPDH aggregates, through a process called nucleocytoplasmic coagulation. Such aggregates can be observed in vivo in the affected tissues of patients with Alzheimer disease or alcoholic liver cirrhosis, or in cell cultures during necrosis. Oxidation at Met-46 may play a pivotal role in the formation of these insoluble structures. This modification has been detected in vitro following treatment with free radical donor (+/-)-(E)-4-ethyl-2-[(E)-hydroxyimino]-5-nitro-3-hexenamide. It has been proposed to destabilize nearby residues, increasing the likelihood of secondary oxidative damages, including oxidation of Tyr-45 and Met-105. This cascade of oxidations may augment GAPDH misfolding, leading to intermolecular disulfide cross-linking and aggregation.
Succination of Cys-152 and Cys-247 by the Krebs cycle intermediate fumarate, which leads to S-(2-succinyl)cysteine residues, inhibits glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. Fumarate concentration as well as succination of cysteine residues in GAPDH is significantly increased in muscle of diabetic mammals. It was proposed that the S-(2-succinyl)cysteine chemical modification may be a useful biomarker of mitochondrial and oxidative stress in diabetes and that succination of GAPDH and other thiol proteins by fumarate may contribute to the metabolic changes underlying the development of diabetes complications.
Cytoplasm>Cytosol. Nucleus. Cytoplasm>Perinuclear region. Membrane. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton.
Note: Translocates to the nucleus following S-nitrosylation and interaction with SIAH1, which contains a nuclear localization signal (By similarity). Postnuclear and Perinuclear regions.
Homotetramer. Interacts with TPPP; the interaction is direct. Interacts (when S-nitrosylated) with SIAH1; leading to nuclear translocation. Interacts with RILPL1/GOSPEL, leading to prevent the interaction between GAPDH and SIAH1 and prevent nuclear translocation. Interacts with CHP1; the interaction increases the binding of CHP1 with microtubules. Associates with microtubules (By similarity). Interacts with EIF1AD, USP25, PRKCI and WARS1. Interacts with phosphorylated RPL13A; inhibited by oxidatively-modified low-densitity lipoprotein (LDL(ox)). Component of the GAIT complex. Interacts with FKBP6; leading to inhibit GAPDH catalytic activity.
The [IL]-x-C-x-x-[DE] motif is a proposed target motif for cysteine S-nitrosylation mediated by the iNOS-S100A8/A9 transnitrosylase complex.
Belongs to the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase family.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Alzheimer's disease.
· Metabolism > Carbohydrate metabolism > Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis.
· Metabolism > Global and overview maps > Metabolic pathways.
· Metabolism > Global and overview maps > Carbon metabolism.
· Metabolism > Global and overview maps > Biosynthesis of amino acids.
References
Application: WB Species: mice Sample: BMDMs
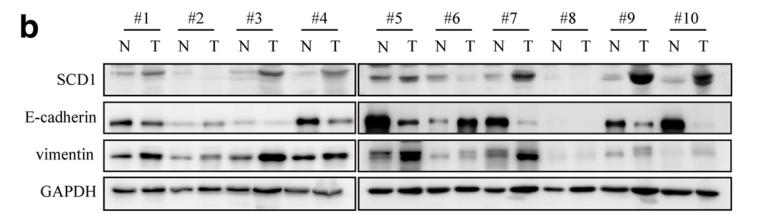
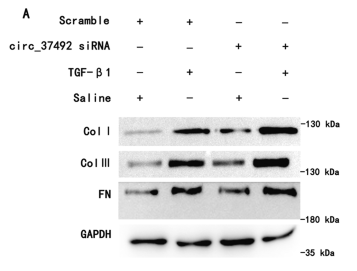
Application: WB Species: human Sample: CRC
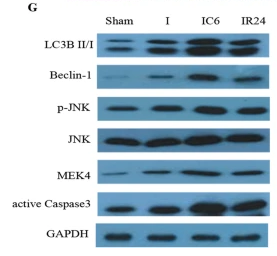
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: spinal dorsal horn
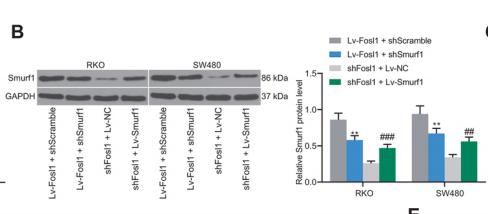
Application: WB Species: human Sample: RKO and SW480 cells
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: BUMPT cells
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.