YB1 Antibody - #AF7832
| Product: | YB1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF7832 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to YB1 |
| Application: | WB |
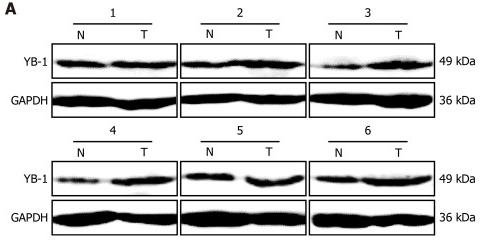
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 50kDa; 36kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P67809 |
| RRID: | AB_2844196 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF7832, RRID:AB_2844196.
Fold/Unfold
BP 8; CBF-A; CCAAT binding transcription factor I subunit A; CCAAT-binding transcription factor I subunit A; CSDA2; CSDB; DBPB; DNA binding protein B; DNA-binding protein B; EFI-A; Enhancer factor I subunit A; MDR NF1; MGC104858; MGC110976; MGC117250; NSEP 1; NSEP1; Nuclease sensitive element binding protein 1; Nuclease-sensitive element-binding protein 1; p50; Q15905; Y-box binding protein 1; Y-box transcription factor; Y-box-binding protein 1; YB 1; YB-1; YBOX1_HUMAN; YBX 1; ybx1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human YB1, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P67809 YBOX1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSSEAETQQPPAAPPAAPALSAADTKPGTTGSGAGSGGPGGLTSAAPAGGDKKVIATKVLGTVKWFNVRNGYGFINRNDTKEDVFVHQTAIKKNNPRKYLRSVGDGETVEFDVVEGEKGAEAANVTGPGGVPVQGSKYAADRNHYRRYPRRRGPPRNYQQNYQNSESGEKNEGSESAPEGQAQQRRPYRRRRFPPYYMRRPYGRRPQYSNPPVQGEVMEGADNQGAGEQGRPVRQNMYRGYRPRFRRGPPRQRQPREDGNEEDKENQGDETQGQQPPQRRYRRNFNYRRRRPENPKPQDGKETKAADPPAENSSAPEAEQGGAE
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
DNA- and RNA-binding protein involved in various processes, such as translational repression, RNA stabilization, mRNA splicing, DNA repair and transcription regulation. Predominantly acts as a RNA-binding protein: binds preferentially to the 5'-[CU]CUGCG-3' RNA motif and specifically recognizes mRNA transcripts modified by C5-methylcytosine (m5C). Promotes mRNA stabilization: acts by binding to m5C-containing mRNAs and recruiting the mRNA stability maintainer ELAVL1, thereby preventing mRNA decay. Component of the CRD-mediated complex that promotes MYC mRNA stability. Contributes to the regulation of translation by modulating the interaction between the mRNA and eukaryotic initiation factors (By similarity). Plays a key role in RNA composition of extracellular exosomes by defining the sorting of small non-coding RNAs, such as tRNAs, Y RNAs, Vault RNAs and miRNAs. Probably sorts RNAs in exosomes by recognizing and binding C5-methylcytosine (m5C)-containing RNAs. Acts as a key effector of epidermal progenitors by preventing epidermal progenitor senescence: acts by regulating the translation of a senescence-associated subset of cytokine mRNAs, possibly by binding to m5C-containing mRNAs. Also involved in pre-mRNA alternative splicing regulation: binds to splice sites in pre-mRNA and regulates splice site selection. Also able to bind DNA: regulates transcription of the multidrug resistance gene MDR1 is enhanced in presence of the APEX1 acetylated form at 'Lys-6' and 'Lys-7'. Binds to promoters that contain a Y-box (5'-CTGATTGGCCAA-3'), such as MDR1 and HLA class II genes. Promotes separation of DNA strands that contain mismatches or are modified by cisplatin. Has endonucleolytic activity and can introduce nicks or breaks into double-stranded DNA, suggesting a role in DNA repair. The secreted form acts as an extracellular mitogen and stimulates cell migration and proliferation.
Ubiquitinated by RBBP6; leading to a decrease of YBX1 transcactivational ability.
In the absence of phosphorylation the protein is retained in the cytoplasm.
Cleaved by a 20S proteasomal protease in response to agents that damage DNA. Cleavage takes place in the absence of ubiquitination and ATP. The resulting N-terminal fragment accumulates in the nucleus (By similarity).
Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasmic granule. Secreted. Secreted>Extracellular exosome.
Note: Predominantly cytoplasmic in proliferating cells (PubMed:12604611). Cytotoxic stress and DNA damage enhance translocation to the nucleus (PubMed:14718551). Localized in cytoplasmic mRNP granules containing untranslated mRNAs (PubMed:25229427). Shuttles between nucleus and cytoplasm (PubMed:25229427). Localized with DDX1, MBNL1 and TIAL1 in stress granules upon stress (PubMed:18335541). Secreted by mesangial and monocytic cells after inflammatory challenges (PubMed:19483673).
In the CSD domain, Trp-65 specifically recognizes C5-methylcytosine (m5C) modification through its indole ring.
Belongs to the YBX1 family.
References
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: liver tissues
Application: IHC Species: Human Sample: liver tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.