SNAP25 Antibody - #AF0254
| Product: | SNAP25 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF0254 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to SNAP25 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 25kDa; 23kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P60880 |
| RRID: | AB_2833429 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF0254, RRID:AB_2833429.
Fold/Unfold
bA416N4.2; Bdr; CMS18; dJ1068F16.2; FLJ23079; HGNC:11132; MGC105414; MGC139754; Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 4 homolog; RIC 4; RIC4; SEC 9; SEC9; SNAP 25; SNAP; SNAP-25; SNAP-25B; SNAP25; SNP 25; SNP25; SNP25_HUMAN; sp; SUP; Super protein; Synaptosomal associated 25 kDa protein; Synaptosomal associated protein; Synaptosomal associated protein 25; Synaptosomal associated protein 25kDa; Synaptosomal-associated 25 kDa protein; Synaptosomal-associated protein 25; Synaptosomal-associated protein, 25-KD;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human SNAP25, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Neurons of the neocortex, hippocampus, piriform cortex, anterior thalamic nuclei, pontine nuclei, and granule cells of the cerebellum.
- P60880 SNP25_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAEDADMRNELEEMQRRADQLADESLESTRRMLQLVEESKDAGIRTLVMLDEQGEQLERIEEGMDQINKDMKEAEKNLTDLGKFCGLCVCPCNKLKSSDAYKKAWGNNQDGVVASQPARVVDEREQMAISGGFIRRVTNDARENEMDENLEQVSGIIGNLRHMALDMGNEIDTQNRQIDRIMEKADSNKTRIDEANQRATKMLGSG
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
t-SNARE involved in the molecular regulation of neurotransmitter release. May play an important role in the synaptic function of specific neuronal systems. Associates with proteins involved in vesicle docking and membrane fusion. Regulates plasma membrane recycling through its interaction with CENPF. Modulates the gating characteristics of the delayed rectifier voltage-dependent potassium channel KCNB1 in pancreatic beta cells.
Palmitoylated. Cys-85 appears to be the main site, and palmitoylation is required for membrane association (By similarity).
(Microbial infection) Targeted and hydrolyzed by C.botulinum neurotoxin type A (BoNT/A, botA) which hydrolyzes the 197-Gln-|-Arg-198 bond and inhibits neurotransmitter release.
(Microbial infection) Targeted and hydrolyzed by C.botulinum neurotoxin type C (BoNT/C) which hydrolyzes the 198-Arg-|-Ala-199 bond and inhibits neurotransmitter release. C.botulinum type C only rarely infects humans.
(Microbial infection) Targeted and hydrolyzed by C.botulinum neurotoxin type E (BoNT/E) which hydrolyzes the 180-Arg-|-Ile-181 bond and inhibits neurotransmitter release.
Cytoplasm>Perinuclear region. Cell membrane>Lipid-anchor. Cell junction>Synapse>Synaptosome. Photoreceptor inner segment.
Note: Membrane association requires palmitoylation. Expressed throughout cytoplasm, concentrating at the perinuclear region. Colocalizes with KCNB1 at the cell membrane (By similarity). Colocalizes with PLCL1 at the cell membrane (By similarity).
Neurons of the neocortex, hippocampus, piriform cortex, anterior thalamic nuclei, pontine nuclei, and granule cells of the cerebellum.
Belongs to the SNAP-25 family.
Research Fields
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Synaptic vesicle cycle.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin secretion. (View pathway)
References
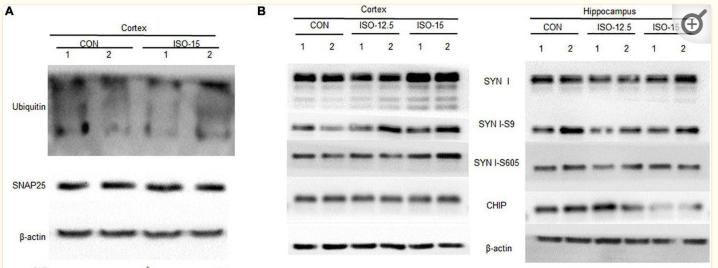
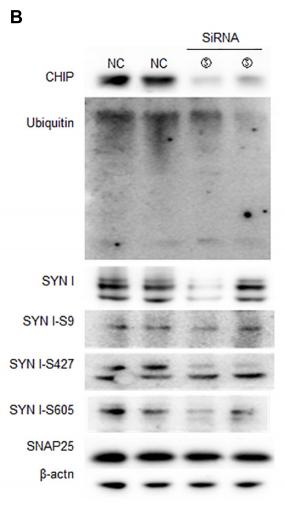
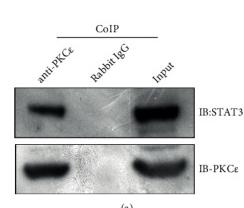
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: spinal cord tissues
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: brain tissue
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: N2a cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.