CDK1/CDC2 Antibody - #AF6108
| Product: | CDK1/CDC2 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6108 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CDK1/CDC2 |
| Application: | WB IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 34kDa; 34kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P06493 |
| RRID: | AB_2834995 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6108, RRID:AB_2834995.
Fold/Unfold
Cdc 2; Cdc2; CDC28A; CDK 1; CDK1; CDK1_HUMAN; CDKN1; CELL CYCLE CONTROLLER CDC2; Cell division control protein 2; Cell division control protein 2 homolog; Cell division cycle 2 G1 to S and G2 to M; Cell division protein kinase 1; Cell Divsion Cycle 2 Protein; Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1; Cyclin-dependent kinase 1; DKFZp686L20222; MGC111195; p34 Cdk1; p34 protein kinase; P34CDC2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CDK1/CDC2, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
- P06493 CDK1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEDYTKIEKIGEGTYGVVYKGRHKTTGQVVAMKKIRLESEEEGVPSTAIREISLLKELRHPNIVSLQDVLMQDSRLYLIFEFLSMDLKKYLDSIPPGQYMDSSLVKSYLYQILQGIVFCHSRRVLHRDLKPQNLLIDDKGTIKLADFGLARAFGIPIRVYTHEVVTLWYRSPEVLLGSARYSTPVDIWSIGTIFAELATKKPLFHGDSEIDQLFRIFRALGTPNNEVWPEVESLQDYKNTFPKWKPGSLASHVKNLDENGLDLLSKMLIYDPAKRISGKMALNHPYFNDLDNQIKKM
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Plays a key role in the control of the eukaryotic cell cycle by modulating the centrosome cycle as well as mitotic onset; promotes G2-M transition, and regulates G1 progress and G1-S transition via association with multiple interphase cyclins. Required in higher cells for entry into S-phase and mitosis. Phosphorylates PARVA/actopaxin, APC, AMPH, APC, BARD1, Bcl-xL/BCL2L1, BRCA2, CALD1, CASP8, CDC7, CDC20, CDC25A, CDC25C, CC2D1A, CENPA, CSNK2 proteins/CKII, FZR1/CDH1, CDK7, CEBPB, CHAMP1, DMD/dystrophin, EEF1 proteins/EF-1, EZH2, KIF11/EG5, EGFR, FANCG, FOS, GFAP, GOLGA2/GM130, GRASP1, UBE2A/hHR6A, HIST1H1 proteins/histone H1, HMGA1, HIVEP3/KRC, LMNA, LMNB, LMNC, LBR, LATS1, MAP1B, MAP4, MARCKS, MCM2, MCM4, MKLP1, MYB, NEFH, NFIC, NPC/nuclear pore complex, PITPNM1/NIR2, NPM1, NCL, NUCKS1, NPM1/numatrin, ORC1, PRKAR2A, EEF1E1/p18, EIF3F/p47, p53/TP53, NONO/p54NRB, PAPOLA, PLEC/plectin, RB1, TPPP, UL40/R2, RAB4A, RAP1GAP, RCC1, RPS6KB1/S6K1, KHDRBS1/SAM68, ESPL1, SKI, BIRC5/survivin, STIP1, TEX14, beta-tubulins, MAPT/TAU, NEDD1, VIM/vimentin, TK1, FOXO1, RUNX1/AML1, SAMHD1, SIRT2 and RUNX2. CDK1/CDC2-cyclin-B controls pronuclear union in interphase fertilized eggs. Essential for early stages of embryonic development. During G2 and early mitosis, CDC25A/B/C-mediated dephosphorylation activates CDK1/cyclin complexes which phosphorylate several substrates that trigger at least centrosome separation, Golgi dynamics, nuclear envelope breakdown and chromosome condensation. Once chromosomes are condensed and aligned at the metaphase plate, CDK1 activity is switched off by WEE1- and PKMYT1-mediated phosphorylation to allow sister chromatid separation, chromosome decondensation, reformation of the nuclear envelope and cytokinesis. Inactivated by PKR/EIF2AK2- and WEE1-mediated phosphorylation upon DNA damage to stop cell cycle and genome replication at the G2 checkpoint thus facilitating DNA repair. Reactivated after successful DNA repair through WIP1-dependent signaling leading to CDC25A/B/C-mediated dephosphorylation and restoring cell cycle progression. In proliferating cells, CDK1-mediated FOXO1 phosphorylation at the G2-M phase represses FOXO1 interaction with 14-3-3 proteins and thereby promotes FOXO1 nuclear accumulation and transcription factor activity, leading to cell death of postmitotic neurons. The phosphorylation of beta-tubulins regulates microtubule dynamics during mitosis. NEDD1 phosphorylation promotes PLK1-mediated NEDD1 phosphorylation and subsequent targeting of the gamma-tubulin ring complex (gTuRC) to the centrosome, an important step for spindle formation. In addition, CC2D1A phosphorylation regulates CC2D1A spindle pole localization and association with SCC1/RAD21 and centriole cohesion during mitosis. The phosphorylation of Bcl-xL/BCL2L1 after prolongated G2 arrest upon DNA damage triggers apoptosis. In contrast, CASP8 phosphorylation during mitosis prevents its activation by proteolysis and subsequent apoptosis. This phosphorylation occurs in cancer cell lines, as well as in primary breast tissues and lymphocytes. EZH2 phosphorylation promotes H3K27me3 maintenance and epigenetic gene silencing. CALD1 phosphorylation promotes Schwann cell migration during peripheral nerve regeneration. CDK1-cyclin-B complex phosphorylates NCKAP5L and mediates its dissociation from centrosomes during mitosis. Regulates the amplitude of the cyclic expression of the core clock gene ARNTL/BMAL1 by phosphorylating its transcriptional repressor NR1D1, and this phosphorylation is necessary for SCF(FBXW7)-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of NR1D1.
(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for hepatitis C virus (HCV) in hepatocytes and facilitates its cell entry.
Phosphorylation at Thr-161 by CAK/CDK7 activates kinase activity. Phosphorylation at Thr-14 and Tyr-15 by PKMYT1 prevents nuclear translocation. Phosphorylation at Tyr-15 by WEE1 and WEE2 inhibits the protein kinase activity and acts as a negative regulator of entry into mitosis (G2 to M transition). Phosphorylation by PKMYT1 and WEE1 takes place during mitosis to keep CDK1-cyclin-B complexes inactive until the end of G2. By the end of G2, PKMYT1 and WEE1 are inactivated, but CDC25A and CDC25B are activated. Dephosphorylation by active CDC25A and CDC25B at Thr-14 and Tyr-15, leads to CDK1 activation at the G2-M transition. Phosphorylation at Tyr-15 by WEE2 during oogenesis is required to maintain meiotic arrest in oocytes during the germinal vesicle (GV) stage, a long period of quiescence at dictyate prophase I, leading to prevent meiotic reentry. Phosphorylation by WEE2 is also required for metaphase II exit during egg activation to ensure exit from meiosis in oocytes and promote pronuclear formation. Phosphorylated at Tyr-4 by PKR/EIF2AK2 upon genotoxic stress. This phosphorylation triggers CDK1 polyubiquitination and subsequent proteolysis, thus leading to G2 arrest. In response to UV irradiation, phosphorylation at Tyr-15 by PRKCD activates the G2/M DNA damage checkpoint.
Polyubiquitinated upon genotoxic stress.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Mitochondrion. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Spindle.
Note: Cytoplasmic during the interphase. Colocalizes with SIRT2 on centrosome during prophase and on splindle fibers during metaphase of the mitotic cell cycle. Reversibly translocated from cytoplasm to nucleus when phosphorylated before G2-M transition when associated with cyclin-B1. Accumulates in mitochondria in G2-arrested cells upon DNA-damage.
Isoform 2 is found in breast cancer tissues.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CDC2/CDKX subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Oocyte meiosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > p53 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Gap junction. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation.
References
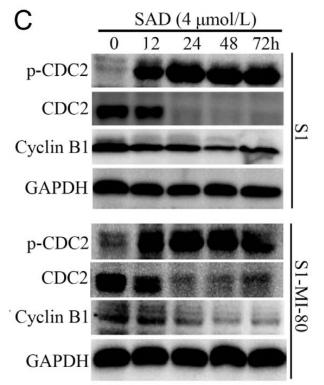
Application: WB Species: human Sample: S1 and S1-MI-80 cells
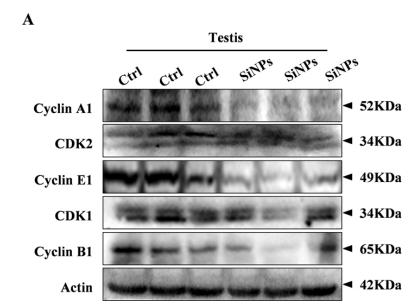
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: testis
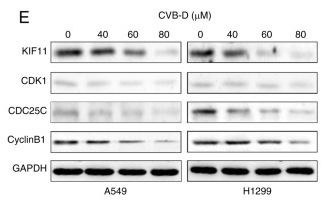
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: NSCLC cells
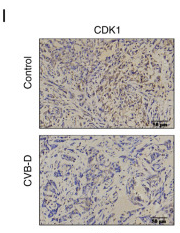
Application: IHC Species: Mouse Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.