Foxp3 Antibody - #AF6544
| Product: | Foxp3 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6544 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Foxp3 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 47kDa; 47kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9BZS1 |
| RRID: | AB_2847268 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6544, RRID:AB_2847268.
Fold/Unfold
AIID; DIETER; Forkhead box P3; Forkhead box protein P3; FOXP3; FOXP3_HUMAN; FOXP3delta7; Immune dysregulation polyendocrinopathy enteropathy X linked; Immunodeficiency polyendocrinopathy enteropathy X linked; IPEX; JM2; MGC141961; MGC141963; OTTHUMP00000025832; OTTHUMP00000025833; OTTHUMP00000226737; PIDX; Scurfin; XPID;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Foxp3.
- Q9BZS1 FOXP3_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MPNPRPGKPSAPSLALGPSPGASPSWRAAPKASDLLGARGPGGTFQGRDLRGGAHASSSSLNPMPPSQLQLPTLPLVMVAPSGARLGPLPHLQALLQDRPHFMHQLSTVDAHARTPVLQVHPLESPAMISLTPPTTATGVFSLKARPGLPPGINVASLEWVSREPALLCTFPNPSAPRKDSTLSAVPQSSYPLLANGVCKWPGCEKVFEEPEDFLKHCQADHLLDEKGRAQCLLQREMVQSLEQQLVLEKEKLSAMQAHLAGKMALTKASSVASSDKGSCCIVAAGSQGPVVPAWSGPREAPDSLFAVRRHLWGSHGNSTFPEFLHNMDYFKFHNMRPPFTYATLIRWAILEAPEKQRTLNEIYHWFTRMFAFFRNHPATWKNAIRHNLSLHKCFVRVESEKGAVWTVDELEFRKKRSQRPSRCSNPTPGP
Research Backgrounds
Transcriptional regulator which is crucial for the development and inhibitory function of regulatory T-cells (Treg). Plays an essential role in maintaining homeostasis of the immune system by allowing the acquisition of full suppressive function and stability of the Treg lineage, and by directly modulating the expansion and function of conventional T-cells. Can act either as a transcriptional repressor or a transcriptional activator depending on its interactions with other transcription factors, histone acetylases and deacetylases. The suppressive activity of Treg involves the coordinate activation of many genes, including CTLA4 and TNFRSF18 by FOXP3 along with repression of genes encoding cytokines such as interleukin-2 (IL2) and interferon-gamma (IFNG). Inhibits cytokine production and T-cell effector function by repressing the activity of two key transcription factors, RELA and NFATC2. Mediates transcriptional repression of IL2 via its association with histone acetylase KAT5 and histone deacetylase HDAC7. Can activate the expression of TNFRSF18, IL2RA and CTLA4 and repress the expression of IL2 and IFNG via its association with transcription factor RUNX1. Inhibits the differentiation of IL17 producing helper T-cells (Th17) by antagonizing RORC function, leading to down-regulation of IL17 expression, favoring Treg development. Inhibits the transcriptional activator activity of RORA. Can repress the expression of IL2 and IFNG via its association with transcription factor IKZF4 (By similarity).
Polyubiquitinated, leading to its proteasomal degradation in regulatory T-cells (Treg) which is mediated by STUB1 in a HSPA1A/B-dependent manner. Deubiquitinated by USP7 leading to increase in protein stability.
Phosphorylation at Ser-418 regulates its transcriptional repressor activity and consequently, regulatory T-cells (Treg) suppressive function. Dephosphorylated at Ser-418 by protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) in Treg cells derived from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Phosphorylation by CDK2 negatively regulates its transcriptional activity and protein stability (By similarity).
Acetylation on lysine residues stabilizes FOXP3 and promotes differentiation of T-cells into induced regulatory T-cells (iTregs) associated with suppressive functions. Deacetylated by SIRT1.
Undergoes proteolytic cleavage in activated regulatory T-cells (Treg), and can be cleaved at either the N- or C-terminal site, or at both sites.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
Note: Predominantly expressed in the cytoplasm in activated conventional T-cells whereas predominantly expressed in the nucleus in regulatory T-cells (Treg). The 41 kDa form derived by proteolytic processing is found exclusively in the chromatin fraction of activated Treg cells (By similarity).
The fork-head DNA-binding domain is essential for its dimerization and interaction with NFATC2.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
References
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
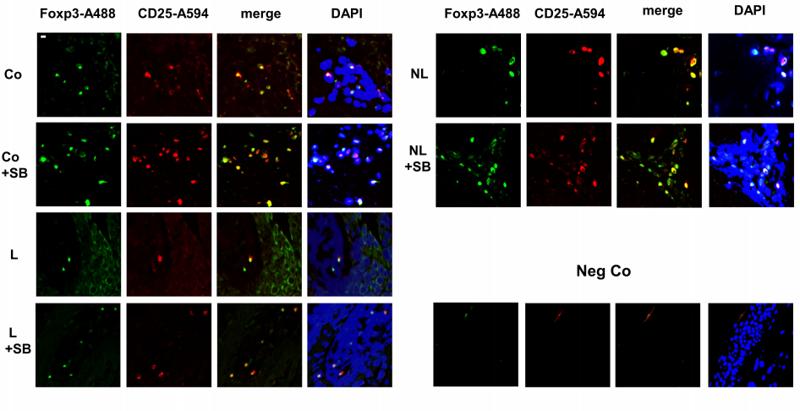
Application: IF/ICC Species: human Sample: PBMC
Application: IF/ICC Species: Human Sample: CRC tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.