GSDMD N-Terminal Antibody(Mouse specific) - #DF13758
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Fold/Unfold
1810036L03Rik; DF 5L; DF5L; DFNA 5L; DFNA5L; FKSG 10; FKSG10; FLJ12150; Gasdermin D; Gasdermin domain containing 1; Gasdermin domain containing protein 1; Gasdermin domain-containing protein 1; Gasdermin-D; GasderminD; GSDMD; GSDMD_HUMAN; GSDMDC 1; GSDMDC1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from Mouse GSDMD.
References
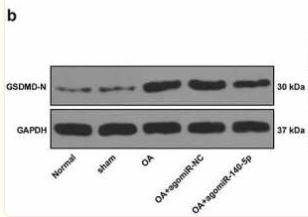
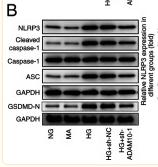
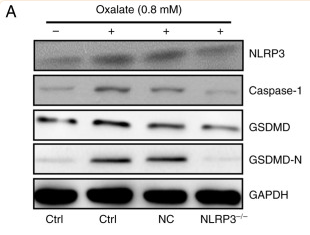
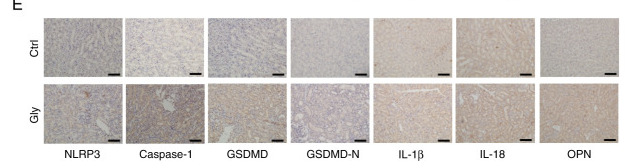
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: CT26 cells
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: livers
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: Colon
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.