MMP13 Antibody - #AF5355
| Product: | MMP13 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5355 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to MMP13 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 54 kDa; 54kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P45452 |
| RRID: | AB_2837840 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5355, RRID:AB_2837840.
Fold/Unfold
CLG 3; CLG3; Collagenase 3; Collagenase3; MANDP1; Matrix metallopeptidase 13 (collagenase 3); Matrix Metalloproteinase 13; Matrix metalloproteinase-13; MMP 13; MMP-13; Mmp13; MMP13_HUMAN;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human MMP13, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
Detected in fetal cartilage and calvaria, in chondrocytes of hypertrophic cartilage in vertebrae and in the dorsal end of ribs undergoing ossification, as well as in osteoblasts and periosteal cells below the inner periosteal region of ossified ribs. Detected in chondrocytes from in joint cartilage that have been treated with TNF and IL1B, but not in untreated chondrocytes. Detected in T lymphocytes. Detected in breast carcinoma tissue.
- P45452 MMP13_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MHPGVLAAFLFLSWTHCRALPLPSGGDEDDLSEEDLQFAERYLRSYYHPTNLAGILKENAASSMTERLREMQSFFGLEVTGKLDDNTLDVMKKPRCGVPDVGEYNVFPRTLKWSKMNLTYRIVNYTPDMTHSEVEKAFKKAFKVWSDVTPLNFTRLHDGIADIMISFGIKEHGDFYPFDGPSGLLAHAFPPGPNYGGDAHFDDDETWTSSSKGYNLFLVAAHEFGHSLGLDHSKDPGALMFPIYTYTGKSHFMLPDDDVQGIQSLYGPGDEDPNPKHPKTPDKCDPSLSLDAITSLRGETMIFKDRFFWRLHPQQVDAELFLTKSFWPELPNRIDAAYEHPSHDLIFIFRGRKFWALNGYDILEGYPKKISELGLPKEVKKISAAVHFEDTGKTLLFSGNQVWRYDDTNHIMDKDYPRLIEEDFPGIGDKVDAVYEKNGYIYFFNGPIQFEYSIWSNRIVRVMPANSILWC
Research Backgrounds
Plays a role in the degradation of extracellular matrix proteins including fibrillar collagen, fibronectin, TNC and ACAN. Cleaves triple helical collagens, including type I, type II and type III collagen, but has the highest activity with soluble type II collagen. Can also degrade collagen type IV, type XIV and type X. May also function by activating or degrading key regulatory proteins, such as TGFB1 and CCN2. Plays a role in wound healing, tissue remodeling, cartilage degradation, bone development, bone mineralization and ossification. Required for normal embryonic bone development and ossification. Plays a role in the healing of bone fractures via endochondral ossification. Plays a role in wound healing, probably by a mechanism that involves proteolytic activation of TGFB1 and degradation of CCN2. Plays a role in keratinocyte migration during wound healing. May play a role in cell migration and in tumor cell invasion.
The proenzyme is activated by removal of the propeptide; this cleavage can be effected by other matrix metalloproteinases, such as MMP2, MMP3 and MMP14 and may involve several cleavage steps. Cleavage can also be autocatalytic, after partial maturation by another protease or after treatment with 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate (APMA) (in vitro).
N-glycosylated.
Tyrosine phosphorylated by PKDCC/VLK.
Secreted>Extracellular space>Extracellular matrix. Secreted.
Detected in fetal cartilage and calvaria, in chondrocytes of hypertrophic cartilage in vertebrae and in the dorsal end of ribs undergoing ossification, as well as in osteoblasts and periosteal cells below the inner periosteal region of ossified ribs. Detected in chondrocytes from in joint cartilage that have been treated with TNF and IL1B, but not in untreated chondrocytes. Detected in T lymphocytes. Detected in breast carcinoma tissue.
The conserved cysteine present in the cysteine-switch motif binds the catalytic zinc ion, thus inhibiting the enzyme. The dissociation of the cysteine from the zinc ion upon the activation-peptide release activates the enzyme (By similarity).
The C-terminal region binds to collagen.
Belongs to the peptidase M10A family.
Research Fields
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
References
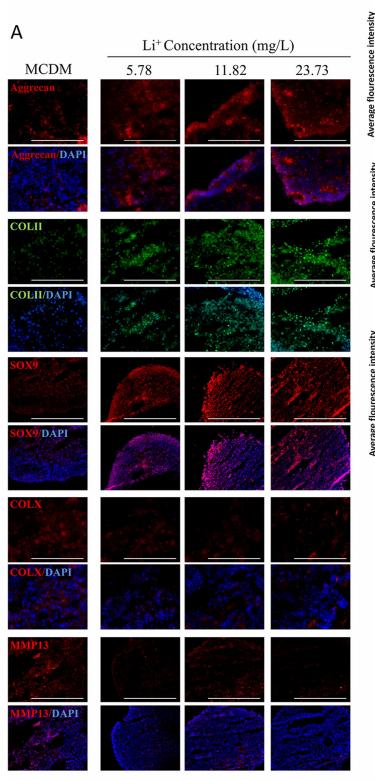
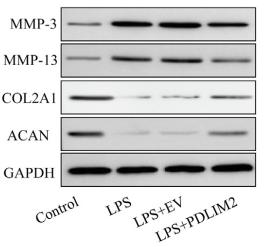
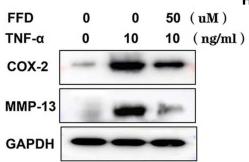
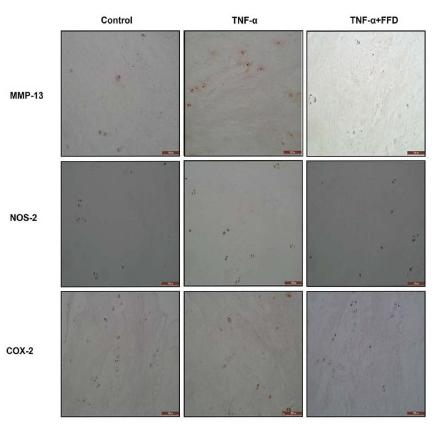
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: IF/ICC Species: Human Sample: iPSCs
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.