FGG Antibody - #DF7432
| Product: | FGG Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7432 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to FGG |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Sheep, Rabbit, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 51kDa; 52kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P02679 |
| RRID: | AB_2839370 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7432, RRID:AB_2839370.
Fold/Unfold
FGG; FIBG_HUMAN; Fibrinogen gamma chain; Fibrinogen gamma polypeptide; fibrinogen gamma-b chain;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human FGG, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P02679 FIBG_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSWSLHPRNLILYFYALLFLSSTCVAYVATRDNCCILDERFGSYCPTTCGIADFLSTYQTKVDKDLQSLEDILHQVENKTSEVKQLIKAIQLTYNPDESSKPNMIDAATLKSRKMLEEIMKYEASILTHDSSIRYLQEIYNSNNQKIVNLKEKVAQLEAQCQEPCKDTVQIHDITGKDCQDIANKGAKQSGLYFIKPLKANQQFLVYCEIDGSGNGWTVFQKRLDGSVDFKKNWIQYKEGFGHLSPTGTTEFWLGNEKIHLISTQSAIPYALRVELEDWNGRTSTADYAMFKVGPEADKYRLTYAYFAGGDAGDAFDGFDFGDDPSDKFFTSHNGMQFSTWDNDNDKFEGNCAEQDGSGWWMNKCHAGHLNGVYYQGGTYSKASTPNGYDNGIIWATWKTRWYSMKKTTMKIIPFNRLTIGEGQQHHLGGAKQVRPEHPAETEYDSLYPEDDL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Together with fibrinogen alpha (FGA) and fibrinogen beta (FGB), polymerizes to form an insoluble fibrin matrix. Has a major function in hemostasis as one of the primary components of blood clots. In addition, functions during the early stages of wound repair to stabilize the lesion and guide cell migration during re-epithelialization. Was originally thought to be essential for platelet aggregation, based on in vitro studies using anticoagulated blood. However, subsequent studies have shown that it is not absolutely required for thrombus formation in vivo. Enhances expression of SELP in activated platelets via an ITGB3-dependent pathway. Maternal fibrinogen is essential for successful pregnancy. Fibrin deposition is also associated with infection, where it protects against IFNG-mediated hemorrhage. May also facilitate the antibacterial immune response via both innate and T-cell mediated pathways.
Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is triggered by thrombin, which cleaves fibrinopeptides A and B from alpha and beta chains, and thus exposes the N-terminal polymerization sites responsible for the formation of the soft clot. The soft clot is converted into the hard clot by factor XIIIA which catalyzes the epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine cross-linking between gamma chains (stronger) and between alpha chains (weaker) of different monomers.
Sulfation of C-terminal tyrosines increases affinity for thrombin.
Secreted.
Detected in blood plasma (at protein level).
A long coiled coil structure formed by 3 polypeptide chains connects the central nodule to the C-terminal domains (distal nodules). The long C-terminal ends of the alpha chains fold back, contributing a fourth strand to the coiled coil structure.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Staphylococcus aureus infection.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Complement and coagulation cascades. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Platelet activation. (View pathway)
References
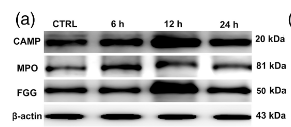
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: Liver
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.