Estrogen Receptor-alpha Antibody - #AF6058
| Product: | Estrogen Receptor-alpha Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6058 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Estrogen Receptor-alpha |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 66kDa,55kDa; 66kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P03372 |
| RRID: | AB_2834976 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6058, RRID:AB_2834976.
Fold/Unfold
DKFZp686N23123; ER alpha; ER; ER-alpha; Era; ESR; ESR1; ESR1_HUMAN; ESRA; Estradiol receptor; Estrogen nuclear receptor alpha; Estrogen receptor 1; Estrogen receptor alpha 3*,4,5,6,7*/822 isoform; Estrogen receptor alpha; Estrogen receptor alpha delta 3*,4,5,6,7*,8*/941 isoform; Estrogen receptor alpha delta 3*,4,5,6,7*/819 2 isoform; Estrogen receptor alpha delta 4 +49 isoform; Estrogen receptor alpha delta 4*,5,6,7*/654 isoform; Estrogen receptor alpha delta 4*,5,6,7,8*/901 isoform; Estrogen receptor alpha E1 E2 1 2; Estrogen receptor alpha E1 N2 E2 1 2; Estrogen receptor; ESTRR; NR3A1; Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group A member 1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Estrogen Receptor-alpha, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
- P03372 ESR1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MTMTLHTKASGMALLHQIQGNELEPLNRPQLKIPLERPLGEVYLDSSKPAVYNYPEGAAYEFNAAAAANAQVYGQTGLPYGPGSEAAAFGSNGLGGFPPLNSVSPSPLMLLHPPPQLSPFLQPHGQQVPYYLENEPSGYTVREAGPPAFYRPNSDNRRQGGRERLASTNDKGSMAMESAKETRYCAVCNDYASGYHYGVWSCEGCKAFFKRSIQGHNDYMCPATNQCTIDKNRRKSCQACRLRKCYEVGMMKGGIRKDRRGGRMLKHKRQRDDGEGRGEVGSAGDMRAANLWPSPLMIKRSKKNSLALSLTADQMVSALLDAEPPILYSEYDPTRPFSEASMMGLLTNLADRELVHMINWAKRVPGFVDLTLHDQVHLLECAWLEILMIGLVWRSMEHPGKLLFAPNLLLDRNQGKCVEGMVEIFDMLLATSSRFRMMNLQGEEFVCLKSIILLNSGVYTFLSSTLKSLEEKDHIHRVLDKITDTLIHLMAKAGLTLQQQHQRLAQLLLILSHIRHMSNKGMEHLYSMKCKNVVPLYDLLLEMLDAHRLHAPTSRGGASVEETDQSHLATAGSTSSHSLQKYYITGEAEGFPATV
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full-length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
Phosphorylated by cyclin A/CDK2 and CK1. Phosphorylation probably enhances transcriptional activity. Self-association induces phosphorylation. Dephosphorylation at Ser-118 by PPP5C inhibits its transactivation activity. Phosphorylated by LMTK3 in vitro.
Glycosylated; contains N-acetylglucosamine, probably O-linked.
Ubiquitinated; regulated by LATS1 via DCAF1 it leads to ESR1 proteasomal degradation. Deubiquitinated by OTUB1.
Dimethylated by PRMT1 at Arg-260. The methylation may favor cytoplasmic localization. Demethylated by JMJD6 at Arg-260.
Palmitoylated (isoform 3). Not biotinylated (isoform 3).
Palmitoylated by ZDHHC7 and ZDHHC21. Palmitoylation is required for plasma membrane targeting and for rapid intracellular signaling via ERK and AKT kinases and cAMP generation, but not for signaling mediated by the nuclear hormone receptor.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side.
Note: A minor fraction is associated with the inner membrane.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side. Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein.
Note: Associated with the inner membrane via palmitoylation (Probable). At least a subset exists as a transmembrane protein with a N-terminal extracellular domain.
Nucleus. Golgi apparatus. Cell membrane.
Note: Colocalizes with ZDHHC7 and ZDHHC21 in the Golgi apparatus where most probably palmitoylation occurs. Associated with the plasma membrane when palmitoylated.
Widely expressed. Isoform 3 is not expressed in the pituitary gland.
Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal ligand-binding domain. The modulating domain, also known as A/B or AF-1 domain has a ligand-independent transactivation function. The C-terminus contains a ligand-dependent transactivation domain, also known as E/F or AF-2 domain which overlaps with the ligand binding domain. AF-1 and AF-2 activate transcription independently and synergistically and act in a promoter- and cell-specific manner. AF-1 seems to provide the major transactivation function in differentiated cells.
Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR3 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Prolactin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Excretory system > Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption.
References
Application: WB Species: Human Sample:
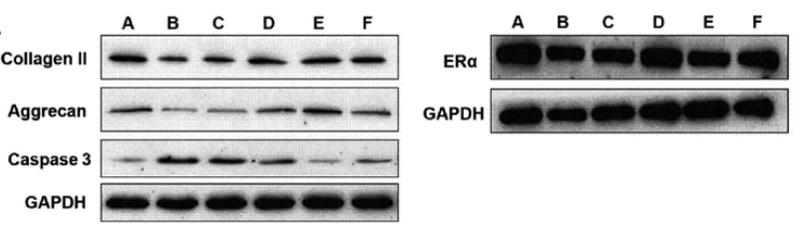
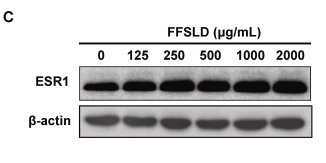
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HepG2 cells
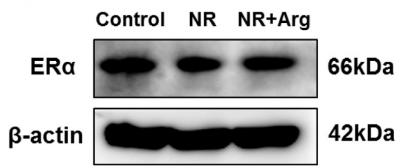
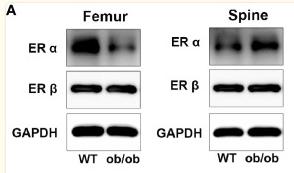
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: femoral and spine
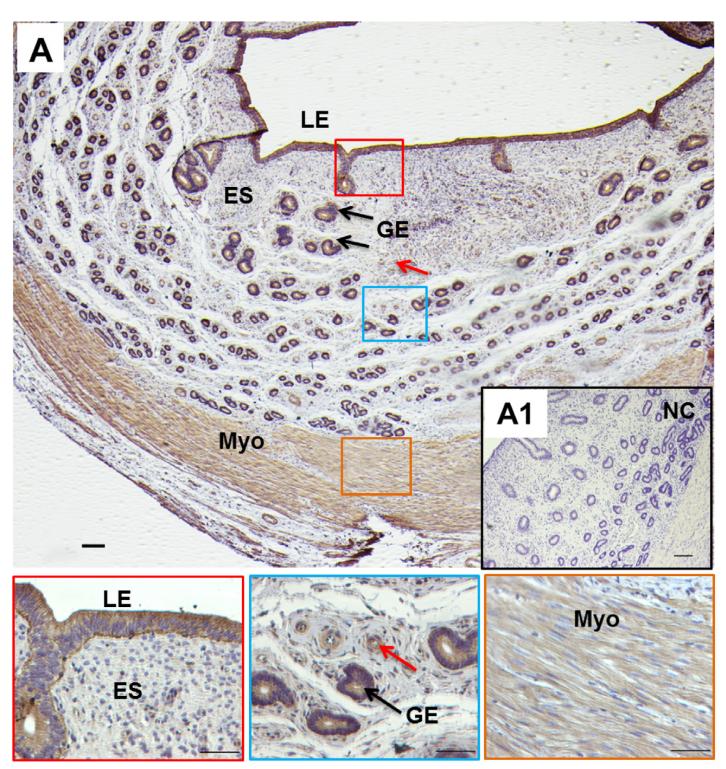
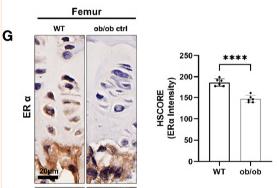
Application: IHC Species: Mice Sample: femoral and vertebral
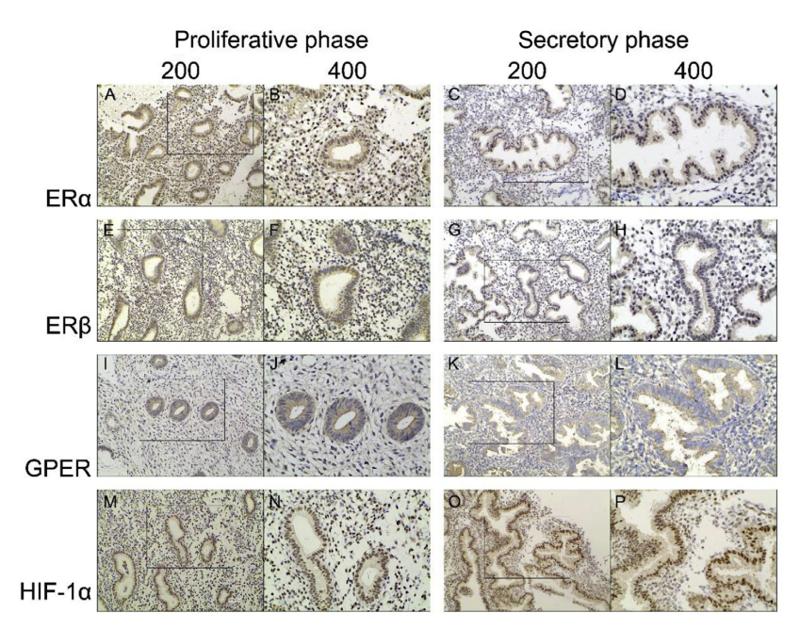
Application: IHC Species: human Sample: endometrium
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.