Tau Antibody - #AF6141
| Product: | Tau Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6141 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Tau |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 50-80kDa; 79kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P10636 |
| RRID: | AB_2835022 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6141, RRID:AB_2835022.
Fold/Unfold
AI413597; AW045860; DDPAC; FLJ31424; FTDP 17; G protein beta1/gamma2 subunit interacting factor 1; MAPT; MAPTL; MGC134287; MGC138549; MGC156663; Microtubule associated protein tau; Microtubule associated protein tau isoform 4; Microtubule-associated protein tau; MSTD; Mtapt; MTBT1; MTBT2; Neurofibrillary tangle protein; Paired helical filament tau; Paired helical filament-tau; PHF tau; PHF-tau; PPND; PPP1R103; Protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 103; pTau; RNPTAU; TAU; TAU_HUMAN; Tauopathy and respiratory failure, included;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Tau, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Expressed in neurons. Isoform PNS-tau is expressed in the peripheral nervous system while the others are expressed in the central nervous system.
- P10636 TAU_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAEPRQEFEVMEDHAGTYGLGDRKDQGGYTMHQDQEGDTDAGLKESPLQTPTEDGSEEPGSETSDAKSTPTAEDVTAPLVDEGAPGKQAAAQPHTEIPEGTTAEEAGIGDTPSLEDEAAGHVTQEPESGKVVQEGFLREPGPPGLSHQLMSGMPGAPLLPEGPREATRQPSGTGPEDTEGGRHAPELLKHQLLGDLHQEGPPLKGAGGKERPGSKEEVDEDRDVDESSPQDSPPSKASPAQDGRPPQTAAREATSIPGFPAEGAIPLPVDFLSKVSTEIPASEPDGPSVGRAKGQDAPLEFTFHVEITPNVQKEQAHSEEHLGRAAFPGAPGEGPEARGPSLGEDTKEADLPEPSEKQPAAAPRGKPVSRVPQLKARMVSKSKDGTGSDDKKAKTSTRSSAKTLKNRPCLSPKHPTPGSSDPLIQPSSPAVCPEPPSSPKYVSSVTSRTGSSGAKEMKLKGADGKTKIATPRGAAPPGQKGQANATRIPAKTPPAPKTPPSSGEPPKSGDRSGYSSPGSPGTPGSRSRTPSLPTPPTREPKKVAVVRTPPKSPSSAKSRLQTAPVPMPDLKNVKSKIGSTENLKHQPGGGKVQIINKKLDLSNVQSKCGSKDNIKHVPGGGSVQIVYKPVDLSKVTSKCGSLGNIHHKPGGGQVEVKSEKLDFKDRVQSKIGSLDNITHVPGGGNKKIETHKLTFRENAKAKTDHGAEIVYKSPVVSGDTSPRHLSNVSSTGSIDMVDSPQLATLADEVSASLAKQGL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Promotes microtubule assembly and stability, and might be involved in the establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity. The C-terminus binds axonal microtubules while the N-terminus binds neural plasma membrane components, suggesting that tau functions as a linker protein between both. Axonal polarity is predetermined by TAU/MAPT localization (in the neuronal cell) in the domain of the cell body defined by the centrosome. The short isoforms allow plasticity of the cytoskeleton whereas the longer isoforms may preferentially play a role in its stabilization.
Phosphorylation at serine and threonine residues in S-P or T-P motifs by proline-directed protein kinases (PDPK1, CDK1, CDK5, GSK3, MAPK) (only 2-3 sites per protein in interphase, seven-fold increase in mitosis, and in the form associated with paired helical filaments (PHF-tau)), and at serine residues in K-X-G-S motifs by MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase (MARK1, MARK2, MARK3 or MARK4), causing detachment from microtubules, and their disassembly. Phosphorylation decreases with age. Phosphorylation within tau/MAP's repeat domain or in flanking regions seems to reduce tau/MAP's interaction with, respectively, microtubules or plasma membrane components. Phosphorylation on Ser-610, Ser-622, Ser-641 and Ser-673 in several isoforms during mitosis. Phosphorylation at Ser-548 by GSK3B reduces ability to bind and stabilize microtubules. Phosphorylation at Ser-579 by BRSK1 and BRSK2 in neurons affects ability to bind microtubules and plays a role in neuron polarization. Phosphorylated at Ser-554, Ser-579, Ser-602, Ser-606 and Ser-669 by PHK. Phosphorylation at Ser-214 by SGK1 mediates microtubule depolymerization and neurite formation in hippocampal neurons. There is a reciprocal down-regulation of phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation. Phosphorylation on Ser-717 completely abolishes the O-GlcNAcylation on this site, while phosphorylation on Ser-713 and Ser-721 reduces glycosylation by a factor of 2 and 4 respectively. Phosphorylation on Ser-721 is reduced by about 41.5% by GlcNAcylation on Ser-717. Dephosphorylated at several serine and threonine residues by the serine/threonine phosphatase PPP5C.
Polyubiquitinated. Requires functional TRAF6 and may provoke SQSTM1-dependent degradation by the proteasome (By similarity). PHF-tau can be modified by three different forms of polyubiquitination. 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination is the major form, 'Lys-6'-linked and 'Lys-11'-linked polyubiquitination also occur.
O-glycosylated. O-GlcNAcylation content is around 8.2%. There is reciprocal down-regulation of phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation. Phosphorylation on Ser-717 completely abolishes the O-GlcNAcylation on this site, while phosphorylation on Ser-713 and Ser-721 reduces O-GlcNAcylation by a factor of 2 and 4 respectively. O-GlcNAcylation on Ser-717 decreases the phosphorylation on Ser-721 by about 41.5%.
Glycation of PHF-tau, but not normal brain TAU/MAPT. Glycation is a non-enzymatic post-translational modification that involves a covalent linkage between a sugar and an amino group of a protein molecule forming ketoamine. Subsequent oxidation, fragmentation and/or cross-linking of ketoamine leads to the production of advanced glycation endproducts (AGES). Glycation may play a role in stabilizing PHF aggregation leading to tangle formation in AD.
Cytoplasm>Cytosol. Cell membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton. Cell projection>Axon. Cell projection>Dendrite.
Note: Mostly found in the axons of neurons, in the cytosol and in association with plasma membrane components.
Expressed in neurons. Isoform PNS-tau is expressed in the peripheral nervous system while the others are expressed in the central nervous system.
The tau/MAP repeat binds to tubulin. Type I isoforms contain 3 repeats while type II isoforms contain 4 repeats.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Alzheimer's disease.
References
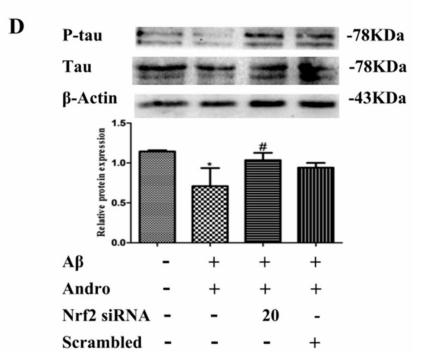
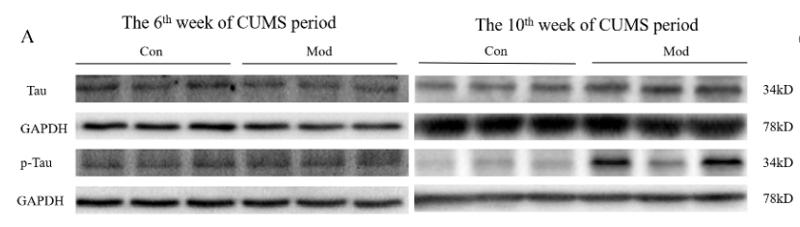
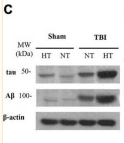
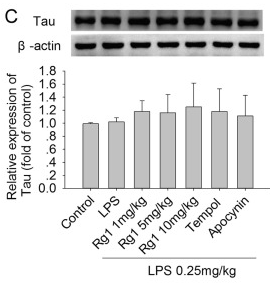
Application: WB Species: Sample: PC12 cells
Application: WB Species: bovine Sample: BMECs
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: brains
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.