CXCR4 Antibody - #AF5279
| Product: | CXCR4 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5279 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CXCR4 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 39 kDa; 40kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P61073 |
| RRID: | AB_2837765 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5279, RRID:AB_2837765.
Fold/Unfold
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; CD184; CD184 antigen; Chemokine (C X C motif) receptor 4; Chemokine CXC Motif Receptor 4; CXC-R4; CXCR-4; CXCR4; CXCR4_HUMAN; D2S201E; FB22; Fusin; HM89; HSY3RR; LAP 3; LAP3; LCR1; LESTR; Leukocyte derived seven transmembrane domain receptor; Leukocyte-derived seven transmembrane domain receptor; Lipopolysaccharide associated protein 3; Neuropeptide Y receptor Y3; NPY3R; NPYR; NPYRL; NPYY3; NPYY3R; Probable G protein coupled receptor lcr1 homolog; SDF 1 receptor; SDF-1 receptor; SEVEN-TRANSMEMBRANE-SEGMENT RECEPTOR; Stromal cell derived factor 1 receptor; Stromal cell-derived factor 1 receptor; WHIM; WHIMS;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CXCR4, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Expressed in numerous tissues, such as peripheral blood leukocytes, spleen, thymus, spinal cord, heart, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, pancreas, cerebellum, cerebral cortex and medulla (in microglia as well as in astrocytes), brain microvascular, coronary artery and umbilical cord endothelial cells. Isoform 1 is predominant in all tissues tested.
- P61073 CXCR4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEGISIYTSDNYTEEMGSGDYDSMKEPCFREENANFNKIFLPTIYSIIFLTGIVGNGLVILVMGYQKKLRSMTDKYRLHLSVADLLFVITLPFWAVDAVANWYFGNFLCKAVHVIYTVNLYSSVLILAFISLDRYLAIVHATNSQRPRKLLAEKVVYVGVWIPALLLTIPDFIFANVSEADDRYICDRFYPNDLWVVVFQFQHIMVGLILPGIVILSCYCIIISKLSHSKGHQKRKALKTTVILILAFFACWLPYYIGISIDSFILLEIIKQGCEFENTVHKWISITEALAFFHCCLNPILYAFLGAKFKTSAQHALTSVSRGSSLKILSKGKRGGHSSVSTESESSSFHSS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Receptor for the C-X-C chemokine CXCL12/SDF-1 that transduces a signal by increasing intracellular calcium ion levels and enhancing MAPK1/MAPK3 activation. Involved in the AKT signaling cascade. Plays a role in regulation of cell migration, e.g. during wound healing. Acts as a receptor for extracellular ubiquitin; leading to enhanced intracellular calcium ions and reduced cellular cAMP levels. Binds bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) et mediates LPS-induced inflammatory response, including TNF secretion by monocytes. Involved in hematopoiesis and in cardiac ventricular septum formation. Also plays an essential role in vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract, probably by regulating vascular branching and/or remodeling processes in endothelial cells. Involved in cerebellar development. In the CNS, could mediate hippocampal-neuron survival (By similarity).
(Microbial infection) Acts as a coreceptor (CD4 being the primary receptor) for human immunodeficiency virus-1/HIV-1 X4 isolates and as a primary receptor for some HIV-2 isolates. Promotes Env-mediated fusion of the virus.
Phosphorylated on agonist stimulation. Rapidly phosphorylated on serine and threonine residues in the C-terminal. Phosphorylation at Ser-324 and Ser-325 leads to recruitment of ITCH, ubiquitination and protein degradation.
Ubiquitinated after ligand binding, leading to its degradation. Ubiquitinated by ITCH at the cell membrane on agonist stimulation. The ubiquitin-dependent mechanism, endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT), then targets CXCR4 for lysosomal degradation. This process is dependent also on prior Ser-/Thr-phosphorylation in the C-terminal of CXCR4. Also binding of ARRB1 to STAM negatively regulates CXCR4 sorting to lysosomes though modulating ubiquitination of SFR5S.
Sulfation on Tyr-21 is required for efficient binding of CXCL12/SDF-1alpha and promotes its dimerization. Tyr-7 and Tyr-12 are sulfated in a sequential manner after Tyr-21 is almost fully sulfated, with the binding affinity for CXCL12/SDF-1alpha increasing with the number of sulfotyrosines present. Sulfotyrosines Tyr-7 and Tyr-12 occupy clefts on opposing CXCL12 subunits, thus bridging the CXCL12 dimer interface and promoting CXCL12 dimerization.
O- and N-glycosylated. Asn-11 is the principal site of N-glycosylation. There appears to be very little or no glycosylation on Asn-176. N-glycosylation masks coreceptor function in both X4 and R5 laboratory-adapted and primary HIV-1 strains through inhibiting interaction with their Env glycoproteins. The O-glycosylation chondroitin sulfate attachment does not affect interaction with CXCL12/SDF-1alpha nor its coreceptor activity.
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell junction. Early endosome. Late endosome. Lysosome.
Note: In unstimulated cells, diffuse pattern on plasma membrane. On agonist stimulation, colocalizes with ITCH at the plasma membrane where it becomes ubiquitinated. In the presence of antigen, distributes to the immunological synapse forming at the T-cell-APC contact area, where it localizes at the peripheral and distal supramolecular activation cluster (SMAC).
Expressed in numerous tissues, such as peripheral blood leukocytes, spleen, thymus, spinal cord, heart, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, pancreas, cerebellum, cerebral cortex and medulla (in microglia as well as in astrocytes), brain microvascular, coronary artery and umbilical cord endothelial cells. Isoform 1 is predominant in all tissues tested.
The amino-terminus is critical for ligand binding. Residues in all four extracellular regions contribute to HIV-1 coreceptor activity.
Belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Chemokine signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Axon guidance. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Leukocyte transendothelial migration. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Intestinal immune network for IgA production. (View pathway)
References
Application: IF/ICC Species: human Sample: breast cancers
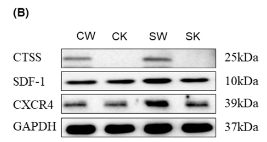
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: BMSCs
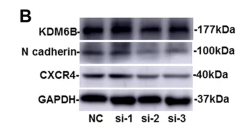
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: UCMSCs
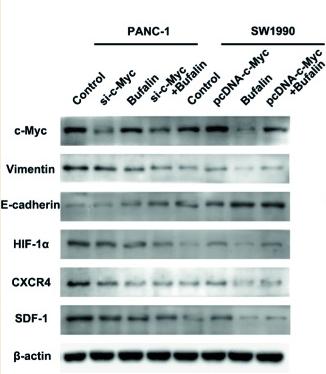
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: pancreatic cancer cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.