CaMKII alpha/delta Antibody - #AF6493
| Product: | CaMKII alpha/delta Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6493 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CaMKII alpha/delta |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 50kDa; 54kD,56kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9UQM7 | Q13557 |
| RRID: | AB_2835304 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6493, RRID:AB_2835304.
Fold/Unfold
Alpha CaMKII; Calcium calmodulin dependent protein kinase II; Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II alpha B subunit; Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase type II alpha chain; Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaM kinase) II alpha; Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha; Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-alpha; Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II subunit alpha; Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IIA; CaM kinase II alpha chain; CaM kinase II alpha subunit; CaM kinase II subunit alpha; CaMK II alpha subunit; CaMK-II subunit alpha; Camk2a; CAMKA; CaMKII; CaMKIINalpha; EC 2.7.11.17; KCC2A_HUMAN; KIAA0968; MGC123320; MGC139375; MGC155201; mKIAA0968; PK2CDD; PKCCD; R74975; zgc:112538; zgc:123320; Calcium / calmodulin dependent protein kinase 2 delta; Calcium / calmodulin dependent protein kinase II delta; calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaM kinase) II delta; calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II delta chain; Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II subunit delta; CAM kinase 2 delta; CAM kinase II delta; CaM kinase II delta subunit; CaM kinase II subunit delta; CaM-kinase II delta chain; CAMK 2d; CaMK-II delta subunit; CaMK-II subunit delta; CAMK2D; CAMKD; CAMKI; KCC2D_HUMAN; RATCAMKI;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CaMK2 alpha/delta, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Expressed in cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle. Isoform Delta 3, isoform Delta 2, isoform Delta 8 and isoform Delta 9 are expressed in cardiac muscle. Isoform Delta 11 is expressed in skeletal muscle.
- Q9UQM7 KCC2A_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MATITCTRFTEEYQLFEELGKGAFSVVRRCVKVLAGQEYAAKIINTKKLSARDHQKLEREARICRLLKHPNIVRLHDSISEEGHHYLIFDLVTGGELFEDIVAREYYSEADASHCIQQILEAVLHCHQMGVVHRDLKPENLLLASKLKGAAVKLADFGLAIEVEGEQQAWFGFAGTPGYLSPEVLRKDPYGKPVDLWACGVILYILLVGYPPFWDEDQHRLYQQIKAGAYDFPSPEWDTVTPEAKDLINKMLTINPSKRITAAEALKHPWISHRSTVASCMHRQETVDCLKKFNARRKLKGAILTTMLATRNFSGGKSGGNKKSDGVKESSESTNTTIEDEDTKVRKQEIIKVTEQLIEAISNGDFESYTKMCDPGMTAFEPEALGNLVEGLDFHRFYFENLWSRNSKPVHTTILNPHIHLMGDESACIAYIRITQYLDAGGIPRTAQSEETRVWHRRDGKWQIVHFHRSGAPSVLPH
- Q13557 KCC2D_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MASTTTCTRFTDEYQLFEELGKGAFSVVRRCMKIPTGQEYAAKIINTKKLSARDHQKLEREARICRLLKHPNIVRLHDSISEEGFHYLVFDLVTGGELFEDIVAREYYSEADASHCIQQILESVNHCHLNGIVHRDLKPENLLLASKSKGAAVKLADFGLAIEVQGDQQAWFGFAGTPGYLSPEVLRKDPYGKPVDMWACGVILYILLVGYPPFWDEDQHRLYQQIKAGAYDFPSPEWDTVTPEAKDLINKMLTINPAKRITASEALKHPWICQRSTVASMMHRQETVDCLKKFNARRKLKGAILTTMLATRNFSAAKSLLKKPDGVKESTESSNTTIEDEDVKARKQEIIKVTEQLIEAINNGDFEAYTKICDPGLTAFEPEALGNLVEGMDFHRFYFENALSKSNKPIHTIILNPHVHLVGDDAACIAYIRLTQYMDGSGMPKTMQSEETRVWHRRDGKWQNVHFHRSGSPTVPIKPPCIPNGKENFSGGTSLWQNI
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that functions autonomously after Ca(2+)/calmodulin-binding and autophosphorylation, and is involved in synaptic plasticity, neurotransmitter release and long-term potentiation. Member of the NMDAR signaling complex in excitatory synapses, it regulates NMDAR-dependent potentiation of the AMPAR and therefore excitatory synaptic transmission (By similarity). Regulates dendritic spine development. Also regulates the migration of developing neurons. Phosphorylates the transcription factor FOXO3 to activate its transcriptional activity.
Autophosphorylation of Thr-286 following activation by Ca(2+)/calmodulin. Phosphorylation of Thr-286 locks the kinase into an activated state.
Cell junction>Synapse. Cell junction>Synapse>Postsynaptic density. Cell projection>Dendritic spine. Cell projection>Dendrite.
Note: Postsynaptic lipid rafts.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CaMK subfamily.
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase involved in the regulation of Ca(2+) homeostatis and excitation-contraction coupling (ECC) in heart by targeting ion channels, transporters and accessory proteins involved in Ca(2+) influx into the myocyte, Ca(2+) release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), SR Ca(2+) uptake and Na(+) and K(+) channel transport. Targets also transcription factors and signaling molecules to regulate heart function. In its activated form, is involved in the pathogenesis of dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Contributes to cardiac decompensation and heart failure by regulating SR Ca(2+) release via direct phosphorylation of RYR2 Ca(2+) channel on 'Ser-2808'. In the nucleus, phosphorylates the MEF2 repressor HDAC4, promoting its nuclear export and binding to 14-3-3 protein, and expression of MEF2 and genes involved in the hypertrophic program. Is essential for left ventricular remodeling responses to myocardial infarction. In pathological myocardial remodeling acts downstream of the beta adrenergic receptor signaling cascade to regulate key proteins involved in ECC. Regulates Ca(2+) influx to myocytes by binding and phosphorylating the L-type Ca(2+) channel subunit beta-2 CACNB2. In addition to Ca(2+) channels, can target and regulate the cardiac sarcolemmal Na(+) channel Nav1.5/SCN5A and the K+ channel Kv4.3/KCND3, which contribute to arrhythmogenesis in heart failure. Phosphorylates phospholamban (PLN/PLB), an endogenous inhibitor of SERCA2A/ATP2A2, contributing to the enhancement of SR Ca(2+) uptake that may be important in frequency-dependent acceleration of relaxation (FDAR) and maintenance of contractile function during acidosis. May participate in the modulation of skeletal muscle function in response to exercise, by regulating SR Ca(2+) transport through phosphorylation of PLN/PLB and triadin, a ryanodine receptor-coupling factor.
Autophosphorylation of Thr-287 following activation by Ca(2+)/calmodulin. Phosphorylation of Thr-287 locks the kinase into an activated state.
Cell membrane>Sarcolemma>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side. Sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side.
Expressed in cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle. Isoform Delta 3, isoform Delta 2, isoform Delta 8 and isoform Delta 9 are expressed in cardiac muscle. Isoform Delta 11 is expressed in skeletal muscle.
The CAMK2 protein kinases contain a unique C-terminal subunit association domain responsible for oligomerization.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CaMK subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Oocyte meiosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Necroptosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Calcium signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > HIF-1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Wnt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Amphetamine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Glioma. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Axon guidance. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Environmental adaptation > Circadian entrainment.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Long-term potentiation.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Neurotrophin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Cholinergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Dopaminergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Sensory system > Olfactory transduction.
· Organismal Systems > Sensory system > Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin secretion. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Melanogenesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Glucagon signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Aldosterone synthesis and secretion.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Gastric acid secretion.
References
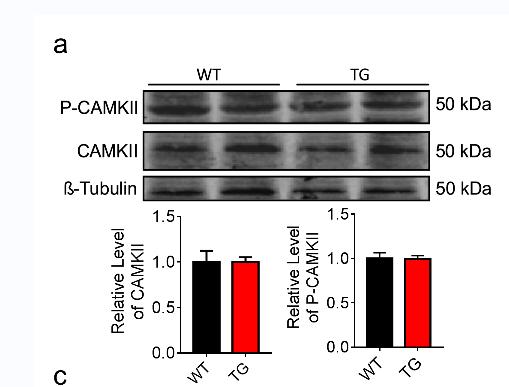
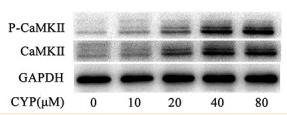
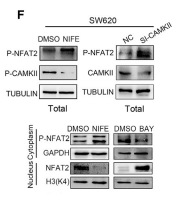
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: Cardiac tissue
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: SH-SY5Y cells
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: TM4 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.