PKA alpha CAT Antibody - #AF5450
| Product: | PKA alpha CAT Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF5450 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to PKA alpha CAT |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Dog, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 36 kDa; 41kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P17612 |
| RRID: | AB_2837934 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5450, RRID:AB_2837934.
Fold/Unfold
cAMP dependent protein kinase alpha catalytic subunit; cAMP dependent protein kinase beta catalytic subunit; cAMP dependent protein kinase catalytic beta subunit isoform 4ab; cAMP dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha; cAMP dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha, isoform 1; cAMP dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta; cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha; KAPCA_HUMAN; PKA C alpha; PKA C beta; PKA C-alpha; PKACA; PKACB; PPNAD4; PRKACA; PRKACAA; PRKACB; Protein kinase A catalytic subunit alpha; Protein kinase A catalytic subunit; Protein kinase A catalytic subunit beta; Protein kinase, cAMP dependent, catalytic, alpha; Protein kinase, cAMP dependent, catalytic, beta;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human PKA alpha CAT, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Isoform 1 is ubiquitous. Isoform 2 is sperm-specific and is enriched in pachytene spermatocytes but is not detected in round spermatids.
- P17612 KAPCA_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MGNAAAAKKGSEQESVKEFLAKAKEDFLKKWESPAQNTAHLDQFERIKTLGTGSFGRVMLVKHKETGNHYAMKILDKQKVVKLKQIEHTLNEKRILQAVNFPFLVKLEFSFKDNSNLYMVMEYVPGGEMFSHLRRIGRFSEPHARFYAAQIVLTFEYLHSLDLIYRDLKPENLLIDQQGYIQVTDFGFAKRVKGRTWTLCGTPEYLAPEIILSKGYNKAVDWWALGVLIYEMAAGYPPFFADQPIQIYEKIVSGKVRFPSHFSSDLKDLLRNLLQVDLTKRFGNLKNGVNDIKNHKWFATTDWIAIYQRKVEAPFIPKFKGPGDTSNFDDYEEEEIRVSINEKCGKEFSEF
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Phosphorylates a large number of substrates in the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Regulates the abundance of compartmentalized pools of its regulatory subunits through phosphorylation of PJA2 which binds and ubiquitinates these subunits, leading to their subsequent proteolysis. Phosphorylates CDC25B, ABL1, NFKB1, CLDN3, PSMC5/RPT6, PJA2, RYR2, RORA and VASP. RORA is activated by phosphorylation. Required for glucose-mediated adipogenic differentiation increase and osteogenic differentiation inhibition from osteoblasts. Involved in the regulation of platelets in response to thrombin and collagen; maintains circulating platelets in a resting state by phosphorylating proteins in numerous platelet inhibitory pathways when in complex with NF-kappa-B (NFKB1 and NFKB2) and I-kappa-B-alpha (NFKBIA), but thrombin and collagen disrupt these complexes and free active PRKACA stimulates platelets and leads to platelet aggregation by phosphorylating VASP. Prevents the antiproliferative and anti-invasive effects of alpha-difluoromethylornithine in breast cancer cells when activated. RYR2 channel activity is potentiated by phosphorylation in presence of luminal Ca(2+), leading to reduced amplitude and increased frequency of store overload-induced Ca(2+) release (SOICR) characterized by an increased rate of Ca(2+) release and propagation velocity of spontaneous Ca(2+) waves, despite reduced wave amplitude and resting cytosolic Ca(2+). PSMC5/RPT6 activation by phosphorylation stimulates proteasome. Negatively regulates tight junctions (TJs) in ovarian cancer cells via CLDN3 phosphorylation. NFKB1 phosphorylation promotes NF-kappa-B p50-p50 DNA binding. Involved in embryonic development by down-regulating the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway that determines embryo pattern formation and morphogenesis. Prevents meiosis resumption in prophase-arrested oocytes via CDC25B inactivation by phosphorylation. May also regulate rapid eye movement (REM) sleep in the pedunculopontine tegmental (PPT). Phosphorylates APOBEC3G and AICDA. Isoform 2 phosphorylates and activates ABL1 in sperm flagellum to promote spermatozoa capacitation. Phosphorylates HSF1; this phosphorylation promotes HSF1 nuclear localization and transcriptional activity upon heat shock.
Asn-3 is partially deaminated to Asp giving rise to 2 major isoelectric variants, called CB and CA respectively.
Autophosphorylated. Phosphorylation is enhanced by vitamin K(2). Phosphorylated on threonine and serine residues. Phosphorylation on Thr-198 is required for full activity.
Phosphorylated at Tyr-331 by activated receptor tyrosine kinases EGFR and PDGFR; this increases catalytic efficiency.
Cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Nucleus. Mitochondrion. Membrane>Lipid-anchor.
Note: Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (PubMed:21085490).
Cell projection>Cilium>Flagellum. Cytoplasmic vesicle>Secretory vesicle>Acrosome.
Note: Expressed in the midpiece region of the sperm flagellum (PubMed:10906071). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity).
Isoform 1 is ubiquitous. Isoform 2 is sperm-specific and is enriched in pachytene spermatocytes but is not detected in round spermatids.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. cAMP subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Oocyte meiosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Gap junction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Calcium signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Wnt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hedgehog signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Parkinson's disease.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Prion diseases.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Cocaine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Amphetamine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Morphine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Alcoholism.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Vibrio cholerae infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Amoebiasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Chemokine signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Vascular smooth muscle contraction. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Platelet activation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Environmental adaptation > Circadian entrainment.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Long-term potentiation.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Glutamatergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Cholinergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Serotonergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > GABAergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Dopaminergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Sensory system > Olfactory transduction.
· Organismal Systems > Sensory system > Taste transduction.
· Organismal Systems > Sensory system > Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin secretion. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Ovarian steroidogenesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Melanogenesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone synthesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Glucagon signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Renin secretion.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Aldosterone synthesis and secretion.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Excretory system > Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption.
· Organismal Systems > Excretory system > Vasopressin-regulated water reabsorption.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Salivary secretion.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Gastric acid secretion.
References
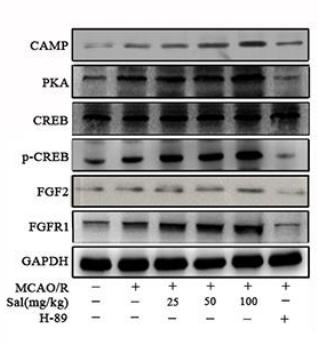
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
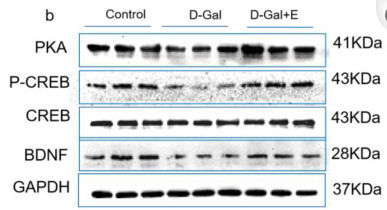
Application: WB Species: rat Sample:
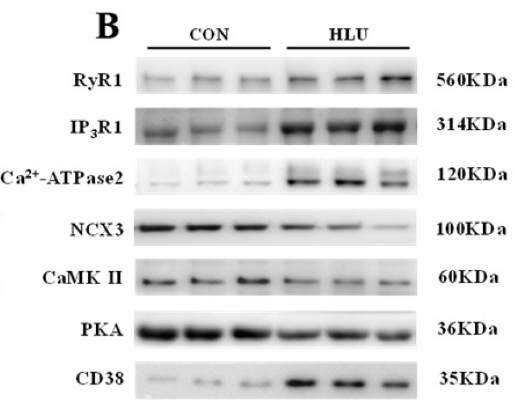
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: hippocampus
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.